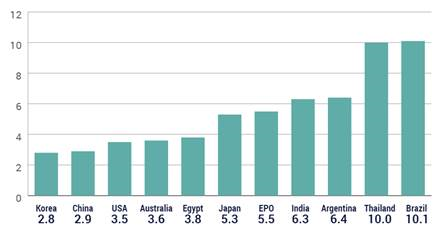
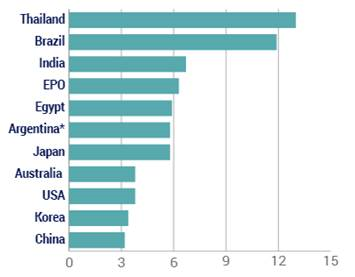
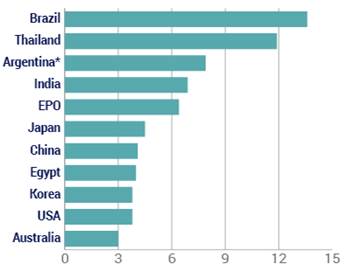
This is the first in a series of posts summarizing CPIP’s 2016 Fall Conference, “Intellectual Property & Global Prosperity.“ The conference was held at Antonin Scalia Law School, George Mason University on October 6-7, 2016. Videos of the conference panels and keynote address, as well as other materials, are available on the conference website.
This is the first in a series of posts summarizing CPIP’s 2016 Fall Conference, “Intellectual Property & Global Prosperity.“ The conference was held at Antonin Scalia Law School, George Mason University on October 6-7, 2016. Videos of the conference panels and keynote address, as well as other materials, are available on the conference website.
The opening panel of CPIP’s 2016 Fall Conference examined how intellectual property (IP) creates opportunities for startups and creative upstarts. Unfortunately, IP policy debates often refer to a misguided notion that intellectual property hinders innovation and creativity, especially among smaller businesses. The panelists, Prof. Deepak Hegde (NYU Stern School of Business), Brian Detwiler (Cobro Ventures, Inc.), Prof. Jerry Liu (University of San Francisco School of Law), and Antigone Peyton (Cloudigy Law, PLLC), illustrated how this notion ignores the fact that intellectual property provides incentives and security for startups and small businesses entering the market and enables returns on investments.
Prof. Deepak Hegde discussed a study he undertook to measure the extent that patents benefit startups. Patents provide incentives for innovation by affording the right to exclude others from making, selling, or otherwise using the patented invention. This incentive is ensured by increasing the cost of imitations, while facilitating licensing and access to venture capital by innovators. At the same time, there is a concern that patents are not as effective for smaller entrepreneurs because patents take too long to issue (three years on average), they are costly to obtain ($20,000 in patent application costs on average), and are expensive to enforce once infringed. The study, however, shows that timely patents do substantially benefit startups.
Hegde noted that measuring the causal effect of patent rights on startups is often an empirically challenging task due to the lack of complete data on issues like rejected patent applications, firm outcomes, and correlations between patenting and startup success. However, Hegde was able to show a positive causal relationship between approval of the first patent application and various measures of startup success such as persistent employment growth and higher sales.
For instance, Hegde found that approval of the first patent application by a medium-sized firm with eight employees leads to three more employees (on average) hired within the five years following approval. Likewise, a medium-sized firm with $4.3M in revenue has $2.3M higher sales over the five years following approval of its first patent. Moreover, approval of the first patent application leads to a 66.4% increase in the number of subsequent applications, a 48.4% growth in the number of approved patents, and a 68.5% increase in the number of total citations.
On the other hand, Hegde discovered that delays in the patent approval process reduce sales growth, with each year of delay reducing growth by 28.4% over the five years following approval. Delays also reduce the quality and quantity of subsequent innovations, with a 14% decrease in number of subsequent applications and a 8% reduction in number of total citations. Even more so, a five-year approval delay is comparable in effect to not granting a patent at all. Finally, Hegde showed that patent approvals causally increase the probability of venture capital funding by 57%, and thus, help to set startups on a growth path.
Brian Detwiler discussed the challenges startups face from a more practical point of view. Specifically, Detwiler focused on two startups that Cobro Ventures is currently managing. Measures of success differ among the two. For a health & fitness center, the issue is profitability, and for a tech startup, the concern is typically acquisition or an initial public offering. Because Cobro Ventures is a self-funded company, it does not encounter some of the funding challenges as other startups. It does, however, face the same intellectual property issues as others in the industry.
The critical issue for a startup in the fitness industry, Detwiler noted, is building a strong brand identity to distinguish itself from other companies in the crowded marketplace. CrossFit is one good example of how a strong brand makes a business successful: CrossFit generates its revenues solely from licensing its brand out to gyms and fitness centers, without operating any of its own.
Tech startups, continued Detwiler, are more invested in the value of their patents because patent due diligence is a major component of any tech acquisition. Bundles of patents and open continuations are what acquirers value the most. The former allows acquisition of all patents associated with a particular technology; the latter provides opportunities to expand claims to pending patents down the road. A patent by itself does not necessarily guarantee the merit of a particular technology, but it certainly shows that at least the Patent Office believes that the particular technology was unique in the marketplace at the time of issuance. Patents can also be used as weapons in protecting a company’s interests and as a bargaining chip in negotiations.
Detwiler stated that trademark registration is equally accessible to startups and big corporations because it is inexpensive (the filing fee is about $300 per class of goods/services), easy to file (only 10 minutes), and fast (around 3-4 months). With patents, the biggest challenge is getting a notice of allowance. There is a common misconception that all patent applications have the same value. This may be true for big corporations that file thousands of patent applications each year. But for startups, which usually have only two or three applications that they depend on, each such application is incredibly important, and if rejected, causes a lot of frustration.
Even though startups have more executive involvement in the patent approval process and are more willing to accept reasonably narrow claims at the outset, Detwiler said the patent examination process is still too lengthy. To get the best of it, he suggested that applicants explain in plain terms what they want to protect, examiners explain in plain terms what they found in their prior art searches, and both sides explore how to capture the claimed invention.
Prof. Jerry Liu talked about the study he undertook on market incentives and intrinsic motivations in the creative industries, particularly in the Chinese music industry. He focused his study on how online piracy affects the music industry and how real-world artists respond to copyright incentives. According to Liu, the Chinese music industry is significantly underdeveloped as compared to the United States. While the overall Chinese economy is fast approaching the size of the U.S. economy, the Chinese music industry represents only 1.5 % of the U.S. music industry.
Liu found that this outcome has little to do with the overall economic environment in China. Even though the music industry experienced a substantial decline since 2005, the economy as a whole enjoyed about 10% of annual growth. Nor is this a consequence of the infamous censorship system in China. Unlike the music industry, the book industry in China has demonstrated growth by 129% for the last decade. The likely reason for this difference is that the piracy rate in the music market is much higher than it is in the book market.
Empirical data collected by Liu establishes the correlation between online piracy and the Chinese music industry downturn. Online piracy surged in 2005, the very same year when music production started to decline significantly. As a result of such widespread piracy, music products have become undervalued among consumers. Only 25.4% of Chinese consumers are willing to pay for music, and only 5.9% actually pay for music. Online piracy has also caused a significant imbalance in the development of the digital music market. Notably, the Chinese government itself recently recognized that uncontrolled piracy has devastated the digital music marketplace.
In China, Liu said that online music services, including downloads and streaming, account only for 1% of the total digital market, while mobile sales (e.g., ringtones) hold 99% market share. But only 32.6% of music consumers are accessing music on their mobile devices, while 96.8% of users access music online. This shows that Chinese consumers pay the least for the most popular channel of music consumption. Additionally, online piracy affects business models in the music industry. For instance, record labels have moved away from their traditional role as investors. They are now working with new artists either on a self-funded basis (labels only provide services and artists bear all the risks of investment) or under so-called “360-degree deals” (labels sign artists for long-term contracts and retain more control over their careers and even their personal lives).
Finally, Liu highlighted the paradox of intrinsic motivations: 92% of the surveyed artists named emotional benefits as their incentive to create, and 97% of those artists also recognized the importance of economic benefits for creation. Importantly, many artists started their career in music not because of the money, but many of them also gave it up because of the money. In this way, copyright protection may provide a powerful incentive for artists to create in that it preserves their artistic freedom while ensuring a decent level of living and a fair return of production costs.
Antigone Peyton talked about strategies for tech companies to protect their assets. In this regard, she noted the importance of contracts at the early stages of the product development cycle. From the copyright prospective, contracts help to establish whether hired developers are employees or independent contractors and to ensure that their rights are assigned to the company. Without a written, explicit assignment of a copyright, a company may get in trouble down the road. For instance, when registering its work with the Copyright Office, enforcing its rights, or selling its assets to a third party.
Peyton stressed that companies working with the government need to understand what intellectual property rights they are giving away and to avoid assigning away all of their rights. Government contracts often include IP provisions that provide the government with a fully-paid license and allow it to bring in another contractor to continue the job. Another important aspect involves privacy policies, especially in the cyber security area. Companies that innovate in this sector usually bring people and know-how to the table, but not necessarily anything that is patentable. To protect its know-how, such a company should consider signing non-compete agreements with the people working with the company.
The barriers to entry for starting up a company in the software industry are small, said Peyton. But that means there are a lot of such companies out there trying to compete with each other for market space. To this end, companies need to think carefully about brand development and brand recognition, as well as how to protect their markets from competitors.
Peyton noted that if a company believes it has patentable subject matter, it should consider filing a patent application early on. However, patenting is the most expensive IP regime and usually requires the help of a patent professional (even with provisional applications). Patents are particularly critical in the biotech, chemical, and pharma industries that are money-intensive endeavors, which largely depend on attracting venture capital investment as early as possible. Generally, tech companies do not need to choose between copyrights and patents, and they may pursue both options to protect their software. But investing in copyrights and brand development is a relatively inexpensive way to start out and build an IP portfolio. Depending on the technology used, trade secret protection may also be an option for tech startups.
Together, the four panelists highlighted how intellectual property has a critical value for startups and small companies in the creative and innovative industries. Not only does IP ignite their businesses, but it also brings opportunities for future growth through sales, licensing, or acquisition. A strong IP portfolio is an invaluable asset, and building it early allows companies to open more doors.
 Last week, CPIP Senior Scholar Adam Mossoff and I filed an amicus brief on behalf of 15 law professors, including CPIP’s Devlin Hartline, Chris Holman, Sean O’Connor, Kristen Osenga, and Mark Schultz. We urge the Supreme Court to grant certiorari in TDE Petroleum v. AKM Enterprise and reaffirm that any analysis of an invention must be of the claimed invention as a whole.
Last week, CPIP Senior Scholar Adam Mossoff and I filed an amicus brief on behalf of 15 law professors, including CPIP’s Devlin Hartline, Chris Holman, Sean O’Connor, Kristen Osenga, and Mark Schultz. We urge the Supreme Court to grant certiorari in TDE Petroleum v. AKM Enterprise and reaffirm that any analysis of an invention must be of the claimed invention as a whole. This is the second in a series of posts summarizing CPIP’s 2016 Fall Conference, “Intellectual Property and Global Prosperity.” The Conference was held at Antonin Scalia Law School, George Mason University on October 6-7, 2016. Videos of the conference panels and keynote address, as well as other materials, are available on the
This is the second in a series of posts summarizing CPIP’s 2016 Fall Conference, “Intellectual Property and Global Prosperity.” The Conference was held at Antonin Scalia Law School, George Mason University on October 6-7, 2016. Videos of the conference panels and keynote address, as well as other materials, are available on the  The Federal Circuit issued another important opinion yesterday affirming that software is a patentable invention in the United States. In
The Federal Circuit issued another important opinion yesterday affirming that software is a patentable invention in the United States. In 
 An oil well drilling rig is not an abstract idea. A method of operating an oil well drilling rig is also not an abstract idea. This proposition should be clear to all, but in
An oil well drilling rig is not an abstract idea. A method of operating an oil well drilling rig is also not an abstract idea. This proposition should be clear to all, but in