The following is taken from a CPIP policy brief by Professor Richard A. Epstein. A PDF of the full policy brief is available here.
Curbing the Abuses of China’s Anti-Monopoly Law:
An Indictment and Reform Agenda
Executive Summary
There are increasing complaints in both the European Union and the United States about a systematic bias in China’s enforcement of its Anti-Monopoly Law (AML). In an extensive report on China’s abuse of its antitrust laws in advancing its own domestic economic policies, for instance, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce noted among many examples a recent action against Microsoft in which Chinese antitrust authorities used a “speculative possibility of licensor hold-up” following Microsoft’s acquisition of Nokia to justify a decree under the AML to “cap license fees for domestic licensees of mobile handset-related software.”
Although the biases in the enforcement of the AML against foreign companies are rooted in systemic problems in China’s political and legal institutions, the abuses are particularly evident in the patent space. FTC Commissioner Joshua Wright has recognized the “growing concern about some antitrust regimes around the world using antitrust laws to further nationalistic goals at the expense of [intellectual property rights] holders, among others.” He specifically mentioned China as one such antitrust regime that may be finding encouragement or at least rationalization in recent FTC and DOJ actions that presume that “special rules for IP are desirable . . . and that business arrangements involving IP rights may be safely presumed to be anticompetitive without rigorous economic analysis and proof of competitive harm.”
This same theme has been recently echoed by FTC Commissioner Maureen Ohlhausen, who explained that recent American decisions on standard essential patents (SEP), such as the FTC’s use of its merger review power to enforce settlement agreements on SEPs against Bosch and Google, have “created potentially confusing precedent for foreign enforcers.” This concern was brought home to her when she witnessed Chinese officials invoke these recent FTC actions against Bosch and Google to justify their per se claim under the AML that “an ‘unreasonable’ refusal to grant a license for a standard essential patent to a competitor should constitute monopolization under the essential facilities doctrine.”
Such broad propositions pave the way for Chinese officials to favor domestic, state-run companies who incorporate foreign patented innovation in their own domestic products and services. These unfettered notions of “unreasonable” conduct become weapons that let Chinese officials force down prices of foreign goods to promote their own nationalist economic policies. Unfortunately, as Commissioner Ohlhausen observed just this past September, recent U.S. antitrust enforcement actions are giving Chinese officials grist for their industrial policy mill.
It is critical that American legal authorities do not give aid and comfort to China’s discriminatory treatment of foreign companies under the AML by the way in which American regulators either speak about or take action on SEPs or other issues relating to patented innovation in this country. The antitrust laws should not be applied so as to single out patents or any other intellectual property rights for special treatment; all property deployed in the marketplace should be treated equally under the competition laws.
The unfortunate situation in China is one example of a dangerous set of practices which could spread to other countries, motivated either by imitating what China has done or retaliating against its abuses. The risk is that the disease can spread all too easily. Until reforms are implemented in both the substance of the AML and the enforcement practices of the Chinese authorities, American policymakers and enforcement authorities should do everything they can to avoid aiding this misuse of antitrust as a domestic economic policy cudgel.
Curbing the Abuses of China’s Anti-Monopoly Law:
An Indictment and Reform Agenda
Richard A. Epstein
I. Introduction
There is a loud chorus of complaints from both the European Union and the United States about a systematic bias in China’s enforcement of its Anti-Monopoly Law (AML). This bias is evident in a wide range of economic sectors and companies. The Economist reports that China has imposed extra-heavy antitrust penalties on foreign automobile manufacturers, such as Daimler, including a record $200 million penalty on a group of ten Japanese car-parts firms, and the New York Times reports that China has imposed another $109 million penalty on six companies selling infant milk formula. China has also initiated antitrust enforcement actions against American high-tech companies, such as Microsoft and Qualcomm, and there is an ongoing Chinese probe of Qualcomm (a firm for which I have consulted unrelated issues), which is said to be done with an effort to force a reduction in the prices that it charges for its advanced wireless technology, which China needs to implement a new 4G system for mobile phones. Similarly, in a wide-ranging report on China’s abuse of the AML to advance domestic industrial policy, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce noted many examples, including a recent action against Microsoft in which Chinese antitrust authorities used its acquisition of Nokia as a basis for a completely “speculative possibility of licensor hold-up” to justify a decree to “cap license fees for domestic licensees of mobile handset-related software.” It is no wonder that many commentators are repeatedly stressing the distinctive foreign focus of China’s recent antitrust activities.
Chinese public officials insist that their stepped-up enforcement of the AML is even-handed. “Everyone is equal before the law,” asserted Li Pumin, the head of the National Development and Reform Commission, which takes the lead in investigating foreign firms. But others in China disagree. More market-oriented Chinese writers have lamented how China’s commitment to market processes has reversed course since the adoption of the AML law, as China is now using this law as an industrial policy cudgel in promoting its own domestic firms at the expense of foreign ones. Its recent behavior, which provoked expressions of concern from American antitrust officials at both the Federal Trade Commission and the Department of Justice, suggests that this is indeed the case.
II. The Chinese Anti-Monopoly Law
The current situation is an unwelcome reversal of the initial optimism that surrounded the adoption of the AML in 2008, and so a quick overview of the AML’s provisions is necessary. Hailed at the time as “a tremendous leap forward for China,” the law adopts, at least in the abstract, many of the standard categories of antitrust analysis found in the United States and in the European Union. In Article 3, it contains the standard prohibitions against horizontal arrangements that raise prices, reduce output, or divide territories, subject to an exemption under Article 15 for agreements that improve technical standards or upgrade consumer products. The AML also bans “abuse of dominant market positions by business operators,” which under Article 17 includes setting prices in “selling commodities at unfairly high prices or buying commodities at unfairly low prices;” or in selling goods at below costs, refusals to deal, and tie-in arrangements, all “without any justifiable cause.”[i]
In many ways what is most notable about the AML is the extent to which it imitates the major features, both good and bad, of the more developed competition law applied in the United States and the European Union. But by the same token, it is quite clear that the Chinese law is embedded in a different set of institutional arrangements. Two elements stand out.
First, the AML reflects the unique Chinese approach to “market socialism” that was first implemented by Deng Xiaoping’s reform policies in the late 1970s as “socialism with Chinese characteristics.” Article 4 of the AML thus attempts to square the circle: “The State constitutes and carries out competition rules which accord with the socialist market economy, perfects macro-control, and advances a unified, open, competitive and orderly market system.”
Second, the socialist legacy reflected in Article 4 has resulted in an extensive system of state-owned industries in China, and Article 7 of the AML provides special controls, exemptions and protections for this sector of the Chinese economy:
Industries controlled by the State-owned economy and concerning the lifeline of national economy and national security or the industries implementing exclusive operation and sales according to law, the state protects the lawful business operations conducted by the business operators therein. The state also lawfully regulates and controls their business operations and the prices of their commodities and services so as to safeguard the interests of consumers and promote technical progresses.
The scope of Article 7 offers instructive clues toward understanding the current situation. Its text refers to entire “industries,” not just individual firms, that are given special treatment under the AML. It still speaks in terms of constraining the ability of “industries” to engage in any abusive practices, which at least in principle serve as the basis for competition-focused anti-monopoly law.
Unfortunately, the odds of it remaining focused in this constructive way are necessarily reduced because of its dual operation with respect to both state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and foreign corporations. The SOEs have a built-in preferential position that can manifest itself in two ways. Either they can get gentle slaps on the wrist for offenses that prompt far harsher sanctions against private companies, especially foreign companies who are either suppliers or competitors with SOEs, or the SOEs could prod Chinese anti-monopoly enforcement authorities to take action against their foreign competitors. The AML can all too easily function as a new form of protectionism by virtue of its differential application to foreign firms vis-à-vis SOEs doing business in China.
The difficulties here are increased, moreover, by the structural decision to parcel out enforcement of the AML to several agencies. The National Development and Reform Commission has the lead with respect to enforcement over monopoly agreements. The State Administration of Industry and Commerce deals with abuses of dominant position. The division of enforcement authority between these agencies makes it much harder to impose uniform standards on the overall operation of the system. This split in enforcement authority increases the risks of differential enforcement and, more worrisome, the misuse or discriminatory use of the AML.
Therefore, it is evident that no evaluation of the operation of the Chinese anti-monopoly system can be made solely on the basis of the statutory terms in the AML itself. So much depends on the oft-concealed enforcement practices of the relevant public authorities, who are given very broad powers of inspection and investigation under AML Article 39, which empowers the AML enforcers to run investigations “by getting into the business premises of business operators under investigation or by getting into any other relevant place,” or by forcing them to respond to interrogatories “to explain the relevant conditions” to the public authorities.” Chinese officials also have the power to examine or duplicate all business papers and to seize and retain relevant evidence, and to examine bank records and accounts. The only procedural protection contained in Article 39, if it can be called that, is that a “written report shall be submitted to the chief person(s)-in-charge of the anti-monopoly authority” before the investigation is approved. What kind of report and how it is to be reviewed are not stated, even though these substantive and procedural issues are subjects of volumes of statutory, regulatory and decisional law on administrative procedure in the United States and Europe. Even more significant, there is no mention anywhere in the AML of any probable cause or warrant requirement that must be demonstrated before any independent judicial body.
III. Rule of Law
At the root of the many complaints about the Chinese approach to competition law is the constant concern that its antitrust enforcement practices are inconsistent with the rule of law. Its legal system invites arbitrary and differential enforcement of anti-monopoly standards. In dealing with these rule of law issues, it is incumbent to note that they address a critical mix of concerns about both substantive standards and administrative enforcement.
As a general rule of thumb, the more precise the particular rules of conduct that receive government enforcement, the better the prospects to avoid both rule of law violations and the general perception of such government violations. In this regard, it is worth noting that the ordinary rules of property, contract and tort score very well under this general standard. As I have argued in my book Design For Liberty: Private Property, Public Administration and the Rule of Law, these common law rules have several key structural features that facilitate rule of law values.
First, the basic norm with respect to private property is that all other persons need only follow the basic norm “keep off” to comply with the system. The simplicity of this command means that anyone can follow it regardless of the size of the polity in which this rule operates. The same command works as well in China with 1.4 billion people as it does in New Zealand with a population just under 4.5 million people.
Second, the content of this simple rule is easily known and understood, so that no one need give special notice of what it requires to the many people who are bound by it. It is no small deal to have a rule that is not promulgated by statute, which is thereafter interpreted by dense pages of administrative text to which the public has only imperfect knowledge, and which both small and large businesses are able to interpret and apply only with the aid of professional intermediaries such as trade associations and law firms.
Third, the simple rule in question works as well in poor countries as in rich ones, so that there is no awkward transition in rules with increasing development over time. At this point, the property rules are complemented by the contract rules that allow people within broad limits to decide their own agreements for the provision of goods and services, so that in most cases the key function of the state is to enforce the agreement as designed, not to improve upon its terms with flights of legislative or judicial fancy.
The Chinese AML does not, and cannot, exhibit anything like the requisite level of overall clarity. In order to determine whether a horizontal arrangement violates the antitrust law, for example, it is necessary to have some sense as to the scope of the market, and the nature of the agreement, to see whether it is or is not in restraint of trade. It is also necessary to gather evidence about practices that can span both continents and years. The AML’s standards for dealing with abusive practices are even looser; for example, there is no clear metric by which to determine whether prices are unfairly high or unfairly low. Another nagging question is what it means under the AML for goods to be sold at below cost, because it is completely unclear if the metric is average or marginal cost. No matter which is chosen, the difficulties of estimation further the scope for abuse of administrative discretion.
This nagging uncertainty about the basic operating rules prompted the late Ronald H. Coase to quip to me long ago in a conversation only partly in jest: “If prices move up in any market, it is surely the result of monopolization. If they remain constant, it is surely the result of market stabilization arrangements. If they go down, it is surely the result of predation” (quoting from memory). Coase’s quip ruefully reflects the modus operandi of the Chinese AML. Since any and all price movements could be associated with some violation of the AML, it follows that in principle no party, and no group of firms, is immune from investigation and criminal prosecution, regardless of how it conducts its own business. And owing to the vastness of the multinational businesses who are targeted, these investigations can exert a large influence on the behavior of firms and on their key employees who bear the brunt of those investigations, where they are subject to the possibility of criminal sanctions in addition to emotional wear and tear.
IV. The Patent Dimension
The dangers of this system are apparent and easily understood. With respect to accusations of secret horizontal arrangements and price gouging arrangements, the risk comes in the form of extensive and exhaustive investigations that are intended to stifle and not promote competition in the marketplace. In dealing with these issues, it is critical that our American legal authorities do not give aid and comfort to China’s aggressive regulation of foreign businesses enterprise by the way in which American regulators address similar issues in this country. We live today in an intensely global environment, and any actions in the United States that overstate the role of the antitrust laws can easily be used as reasons to expand antitrust application overseas.
The point applies to all areas of law, but has especial importance in connection with patents, given that technology that is available in one country is instantly available in all. After the Supreme Court handed down eBay v. MercExchange in 2006, injunctive relief is no longer presumptively available for patent infringement in the United States. As Professor Scott Kieff, now of the International Trade Commission, and I have written, eBay eased the way for Thailand to impose its regime of compulsory licensing for pharmaceutical patents, at far below market rates.
Evidently, decisions like eBay do not go unnoticed by foreign nations, where they set up a climate in which the weak enforcement of patent rights becomes par for the course. That same development happens most emphatically in the crossover area between patent and antitrust law. In general, the proper application of the antitrust law does not single out patents for special treatment of the antitrust laws. A clear articulation of this principle was recently made by FTC Commissioner Joshua D. Wright in his 2014 Milton Handler Lecture: “Does the FTC Have a New IP Agenda,” which stressed the importance of the “parity principle” that states a central tenet in the Department of Justice/Federal Trade Commission 1995 Antitrust Guidelines for the Licensing of Intellectual Property: “Agencies apply the same general antitrust principles to conduct involving intellectual property that they apply to conduct involving any other form of tangible or intangible property.”
The parity principle is critical to successful antitrust enforcement because it places an important fetter on the arbitrary use of government power, which increases greatly if any government, China included, could use a wide catalogue of novel arguments to justify some deviation from the general rule. Indeed, this parity principle is an extension of what I have termed elsewhere as the “carry over” principle, which means that intellectual property rights in general should be based on the rules that are applicable to other forms of property, subject only to deviations required by the distinctive features of property rights in information, which chiefly relates to their finite duration to allow for the widespread dissemination of information. But once that key adjustment is made, the standard rules for property used elsewhere, including the rules for injunctive relief, should continue to apply.
Yet as Commissioner Wright mentioned, recent FTC and DOJ actions presume that “special rules for IP are desirable . . . and that business arrangements involving IP rights may be safely presumed to be anticompetitive without rigorous economic analysis and proof of competitive harm.” Commissioner Wright has also recognized the “growing concern about some antitrust regimes around the world using antitrust laws to further nationalistic goals at the expense of [intellectual property rights] holders, among others.” He specifically mentioned China as one such antitrust regime that may be finding encouragement or at least rationalization in these recent actions against IP owners by American antitrust agencies.
This same theme has been recently echoed by FTC Commissioner Maureen Ohlhausen, who noted how foreign nations invoke “‘competition fig leaves’ to address other domestic issues or concerns.” More specifically, Commissioner Ohlhausen explained how this tendency has manifested itself in the debate over standard essential patents (SEPS), that is those patents that are incorporated in setting key technical standards that allow for the interoperability of various technical devices. She also noted how recent American decisions on SEPs have “created potentially confusing precedent for foreign enforcers.” That concern was brought home when Chinese officials invoked recent FTC enforcement actions against Bosch and Google SEPs to justify a per se claim under the AML that “an ‘unreasonable’ refusal to grant a license for a standard essential patent to a competitor should constitute monopolization under the essential facilities doctrine.” Such broad propositions pave the way for Chinese officials to favor domestic, state-run companies who incorporate foreign patented innovation in their own domestic products and services. These unfettered notions of “unreasonable” conduct become weapons that let Chinese officials force down prices of foreign goods to promote their own nationalist economic policies. Unfortunately, as Commissioner Ohlhausen observed just this past September, recent U.S. antitrust enforcement actions are giving Chinese officials grist for their industrial policy mill, by insisting that their heavy-handed antitrust action against foreign patent owners “has support in U.S. precedent,” such as the Google and Bosh settlements.
V. Enforcement Abuses
The suppression of patent licensing rates charged to domestic Chinese firms is just one example of how the AML enforcers have a built-in invitation to run massively intrusive and expensive investigations into any firms. These investigations are unhampered by any clear legal definition of relevance and are undertaken without regard to the high costs incurred by firms seeking to comply with the officials’ edicts, both administrative and reputational. In some cases, the charge falls within the yawning gap in the AML concerning limits on its enforcement practices. For example, the European Union Chamber of Commerce has found that China engages in administrative intimidation, which is intended to short-circuit formal hearings, and forces parties charged to appear before tribunal hearings without the assistance of counsel and without involving their own governments or chambers of commerce in the process.
It is of course impossible for any academic sitting in the United States to make any estimation of the actual level of abuse in any one individual case. But the simple point here is that the Chinese authorities are already low on credibility because of the way in which they conduct themselves in so many other areas. It takes no great imagination to connect the dots between China’s anti-monopoly investigations of foreign companies doing business in China proper with the Chinese government’s hostile response to the Hong Kong protests against the high-handed way in which Chinese authorities are stifling homegrown democratic activities by insisting on government vetting of all candidates for public office to weed out those who might oppose China’s national agenda. And it takes no great leap in imagination to realize that the same aggressive attitude that China now takes on territorial issues with Vietnam and Japan can spill over to these investigations. It is also well known that China blocks (censors) service supplied by the mainstays of the internet and social media, including Google, Facebook, Wikipedia, and Twitter, which would provide ample opportunity for information about government (and private) abuses to be widely spread.
It also looks as though the lack of any formal protections in the AML investigative process opens up the entire system to these forms of abuse. The lack of any reliable reporting on these matters is consistent with wide-scale abuse because of this simple stylized threat: “Be silent and take your punishment and we shall reduce the penalties. Speak about the matter in public and the penalties will increase.” These threats are all too credible within a tightly run collectivist society. The legal system may give little or no relief, and even if the courts were somehow attuned to the civil liberties and procedural issues, the lack of any clear standards for what counts as either a violation or an appropriate penalty reduces the chances that judicial intervention could be used to slow down an official juggernaut.
VI. Reforms
China needs to do more than make bland and predictable protestations that the AML applies on even terms for all players. The question is how? At the most basic level, one way to get rid of this problem is to spin off all SOEs into private hands, preferably by bona fide auctions, so that there is less risk of political influence displacing the rule of law. That path is of course hampered by China’s explicit commitment to socialist principles in the AML and everywhere else.
There is, however, no reason why that has to create an insuperable barrier. Socialist principles are also inconsistent with private ownership of the means of production, and with the belief that open competition in the marketplace will assure the highest level of social output for any given set of resources. In a sense, the 2007 adoption of the AML itself should be regarded as an implicit rejection of the principles of the socialist economy found in Article 4, because it assumes private companies and a functioning free market. It should take only a little imagination to push the cycle one step further by privatizing key government industries with auctions or other schemes of devolution, and the Chinese government has already proven resourceful in finding ways to explain how such free market reforms are consistent with its preexisting socialist system.
Even if this approach is not undertaken, it should still be possible to make reforms internal to the AML itself that are not likely to reduce its economic benefits but could do much to control its adverse effects. Within the American system, a strong distinction is taken between the horizontal arrangements that are governed under Section 1 of the 1890 Sherman Act and the variety of vertical arrangements that are covered under the monopolization provisions of Section 2. The argument in favor of this distinction turns on the anticipated rate of social return from the enforcement of these two provisions.
With the Section 1 prohibition on contracts in restraint of trade, the nature of the societal loss is generally easy to figure out. The horizontal arrangements that restrict output, raise prices or divide territories do not result only in the transfer of wealth from consumers to producers, but also a reduction in overall social wealth by removing those transactions that could take place for mutual benefit at the competitive price, but which will be foreclosed when the cartel raises its price to the monopoly level. As noted earlier, the Chinese AML tracks that approach, at least on paper. The enforcement questions here are not easy, but since there is a clear sense of what the wrong is, it should be possible to obtain evidence from examining evidence of cooperation, including from disgruntled employees of the given firms. And the matter can be helped along immeasurably by rules that waive treble damages to the first cartel member that reports the cartel practices. These rules apply with great force in the current American enforcement efforts, much of which has been directed toward international cartels.
The dynamics under Section 2 of the Sherman Act are quite different. In these instances, it is hard to develop a simple explanation as to why various kinds of vertical arrangements are harmful to consumer welfare. In many cases, the practices that are undertaken by the dominant firm are also undertaken by their smaller rivals that have no element of market power. The clear implication of this simple point is that the practices that are routinely attacked as restrictive are also practices that have efficiency benefits. Any effort to ban or punish these factors could both stifle useful innovations and distort the competitive balance between firms of different size.
The situation gets even worse when the only charge leveled under the AML is that prices are “unfairly high” or “unfairly low,” which is just asking for trouble. At one level the impetus behind this claim is that certain products are sold at higher (or lower) prices in China than in the United States or the European Union. But these simple price comparisons miss so many of the relevant marketplace complications. Higher prices could stem from higher costs in distribution or in compliance with local laws. Lower prices could result from the simple fact that the fixed costs of producing these goods are allocated to the home market where demand is higher, such that the foreign sales at a lower price improve the welfare of both the firm (which gets a chance to expand markets and recover an additional fraction of its fixed costs) and its Chinese customers, who get the benefit of low prices that forces local firms to reduce their costs. It follows therefore that the Chinese antitrust system could do well to narrow the class of offenses that are said to be practiced by dominant firms, avoiding confusing and unclear terms such as “unfair” prices.
Once a sharper definition of monopolization activities is adopted, it reduces the pressure on the enforcement system to engage in overbroad and unfettered investigations or prosecutions, and thus the risks of massive abuse. Nonetheless, it is a grim fact of life that the investigation of cartel-like behavior is always intrusive, precisely because these arrangements are always carried out in secret, which requires extensive government efforts to ferret them out. But in this regard, it is imperative that China reform its antitrust system for the benefit of both its own citizens and foreign companies investing in China. It should adopt procedural protections that impose some definitive and clear checks on how investigators can behave in ways that avoid both massive human rights violations on the one hand and routine investigative abuses on the other.
At this point, it is necessary to add into Chinese law the same kinds of safeguards that are commonplace in most countries with respect to other forms of criminal investigation, whether crimes of violence or drug offenses, or simple cases of fraud and nondisclosure in financial circles and elsewhere. The point here is that the most dangerous sentence in the English language—“trust me I am from the government”—translates perfectly into Chinese. It is not enough that the abuse stops. It is absolutely imperative that the appearance of abuse ceases as well. Those reforms are not beyond the power of the Chinese legal system to implement, but it will take a long overdue switch from the inquisitorial types of system that socialist countries have found all too congenial in the political and economic sphere.
In urging these major antitrust reforms, it is imperative to put the Chinese position into global perspective. The Chinese government is not the only government that uses its anti-monopoly laws as a cudgel to achieve other political or economic objectives. It has lots of company worldwide. There are, more specifically, other illustrations of abuse in the United States and the European Union. The American system is overly exuberant in its discovery processes, especially with respect to international operations under the 1995 guidelines of the United States Department of Justice and the Federal Trade Commission. It offers shameless protection to American export cartels under the Webb-Pomerene Act, passed in 1918 at the end of World War I, when the need for free trade could hardly have been greater. The European Union thrives on broad definitions of “abuse of dominant position” under Article 102 of its 2009 Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union. The enforcement in many other nations, such as India, with its endless protectionist practices, is also in need of major reform.
In dealing with all these multi-national issues, the fundamental insight is that free trade across international borders offers the best hope for the amelioration of the human condition, especially in developing or underdeveloped countries. It is widely understood that tariffs and other restrictions impede the flow of goods across international borders, which is why the World Trade Organization maintains global free trade as its primary objective. The general attack on explicit entry restrictions by foreign firms and goods has borne much fruit in recent years, although there is still work to be done. But it is precisely because tariffs and other barriers to entry are public and thus verifiable that it is (relatively) easy to control their abuse.
The success of the WTO in controlling these practices does not put to rest the protectionist impulses that have generated too many obstacles to free trade. The differential enforcement of the anti-monopoly laws poses major dangers in this regard, for the same laws that protect against anticompetitive practices are all too often used to achieve the very abuse that they are intended to guard against. Commissioner Ohlhausen bluntly puts the point: “Critics claim that China is using its antitrust law to promote industrial policy.” The unfortunate situation in China is but one example of that dangerous set of practices, which unchecked could spread to other countries, motivated either by imitating what China has done or retaliating against its abuses. The risk is that the disease can spread all too easily. Other nations can protest against these practices. But ultimately it is for China itself to throw aside the shackles that disadvantage foreign firms and the Chinese people alike.
Endnotes:
[i] The AML also contains a prohibition against mergers that lead to “concentration of business operators that eliminates or restricts competition or might be eliminating or restricting competition,” but this is not addressed in this brief essay. These prohibitions cover only a few large transactions, none of which involve ordinary commercial practices that are the subject of the anti-monopoly and abuse of practice provisions at issue in the current applications of the AML.
 Last month, global health initiative UNITAID launched an appeal for suggestions on breaking down barriers that frustrate the progress of public health. UNITAID is a multilateral partnership hosted by the World Health Organization whose mission is to develop systematic approaches to identifying challenges in the treatment of devastating diseases such as HIV, TB, and malaria. The call for suggestions comes as UNITAID launches a renewed effort to improve access to health products for “the needy and vulnerable.”
Last month, global health initiative UNITAID launched an appeal for suggestions on breaking down barriers that frustrate the progress of public health. UNITAID is a multilateral partnership hosted by the World Health Organization whose mission is to develop systematic approaches to identifying challenges in the treatment of devastating diseases such as HIV, TB, and malaria. The call for suggestions comes as UNITAID launches a renewed effort to improve access to health products for “the needy and vulnerable.”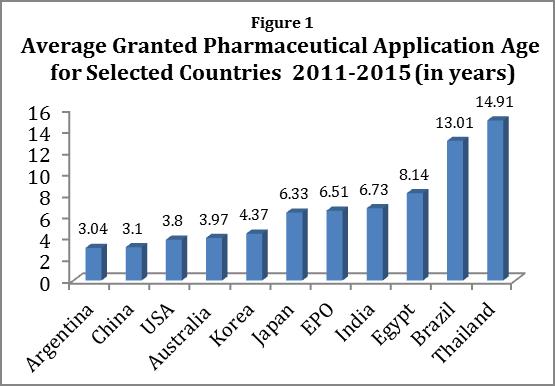
 CPIP has released a new policy brief,
CPIP has released a new policy brief,