Cross-posted from the Mister Copyright blog.
 Last week, the European Court of Justice—the judicial authority of the European Union—issued an anticipated decision in the Sanoma hyperlinking case, declaring that commercial linking with knowledge of unauthorized content constitutes copyright infringement. The opinion comes after years of similar cases in Europe stirred debate over whether linking to pirated works was a ‘communication to the public’ and therefore infringing, and provides a sensible test that protects the works of authors and creators while ensuring the internet remains a bastion of free speech.
Last week, the European Court of Justice—the judicial authority of the European Union—issued an anticipated decision in the Sanoma hyperlinking case, declaring that commercial linking with knowledge of unauthorized content constitutes copyright infringement. The opinion comes after years of similar cases in Europe stirred debate over whether linking to pirated works was a ‘communication to the public’ and therefore infringing, and provides a sensible test that protects the works of authors and creators while ensuring the internet remains a bastion of free speech.
Sanoma involved the popular Dutch news and gossip site GeenStijl, which ran an article in 2011 that included links to an Australian website where copyrighted Playboy magazine photos were made available. The photos were published on the Australian website without the consent of Sanoma, Playboy’s editor and copyright owner of the photos at issues, but taken down after the site was notified of their infringing nature. Despite similar notifications, GeenStijl refused to remove the hyperlinks and actually provided links to another website hosting the unauthorized photos after the Australian website took them down.
Sanoma brought a copyright infringement claim against GS Media, which operates the GeenStijl website, and the Supreme Court of the Netherlands sought a preliminary ruling from the European Court of Justice on whether hyperlinks represent the communication of a work to the public. According to an earlier EU directive, any communication to the public of works protected by copyright must be authorized by the copyright owner. Due to the ubiquity of links and hyperlinks on the Internet, a ruling classifying them as communications to the public would have major ramifications for anyone linking to unauthorized content.
In its judgment, the European Court of Justice found that the concept of ‘communication to the public’ requires individual assessment and laid out the following three factors that must be considered when determining whether a link or hyperlink qualifies.
1) The deliberate nature of the intervention – According to the Court, “the user makes an act of communication when it intervenes, in full knowledge of the consequences of its actions, in order to give access to a protected work to its customers.”
2) The concept of the ‘public’ covers an indeterminate number of potential viewers and implies a large number of people.
3) The profit-making nature of a communication to the public – The Court explains that when hyperlinks are posted for profit, “it may be expected that the person who posted such a link should carry out the checks necessary to ensure that the work concerned is not illegally published.”
Applying these criteria to Sanoma, the Court found that because GS Media runs a commercial website that makes money from advertising, it is undisputed that they posted the hyperlinks for profit, and that it is also undisputed that Sanoma had not authorized the publication of the photos. It also found that because they were notified by Sanoma and continued to repost links after the original source website took down the content, GS Media was aware of the infringing nature of the photos and “cannot, therefore, rebut the presumption that it posted those links in full knowledge of the illegal nature of that publication.” The Court concluded that by posting the links, GS Media therefor effected a ‘communication to the public.’
The Court goes on to detail its desire to maintain a fair balance between the interest of copyright owners and authors and the protection of the interests and fundamental rights of Internet users, “in particular their freedom of expression and of information, as well as the general interest.” After providing the criteria for assessing whether a link qualifies as a communication to the public, the opinion emphasizes the important role hyperlinks play in the exchange and free flow of information over the internet, and clarifies that linking—even to unauthorized content—is not a communication to the public if there is no profit motive or knowledge of the infringing nature of the linked-to works. Even so, it’s important to note that not-for-profit hyperlinking may still be considered a communication to the public if the person posting the link knew or should have reasonably known that the content was posted without authorization.
Perhaps most surprising about the Court’s decree is the relative approval by both copyright owners and supporters of the rights of those posting links. While it speaks to the reasonable approach the Court has taken in determining what qualifies as a communication to the public, it may also represent a hesitation to condemn or praise the order due to a significant ambiguity. It’s not entirely clear who carries the evidentiary burden of proving whether an individual knew or should have reasonably known certain content was posted on the Internet without authorization. If copyright owners and authors are forced to prove a user knew or should have known content was unauthorized every time they attempt to remove links that can appear online incessantly, it could render the new directives ineffectual in protecting creative works.
Regardless of the uncertainly surrounding this burden of proof, the current test seems to strike a balance that holds commercial websites more accountable, while allowing for some flexibility for the general public. With debates over the effectiveness of notice and takedown intensifying in the United States, the EU’s decision on communications to the public should be recognized as workable approach to dealing with infringing hyperlinks. As the United States Copyright Office admits in its 2016 study on the making available right, jurisprudence in the US regarding offering access to content hosted elsewhere on the Internet through hyperlinking is less developed as some foreign jurisdictions. But the study acknowledges the progress made in the EU, and emphasizes the need to include ‘offers of access’ in the crucial making available right.
Despite semantic differences, the EU and the US are both moving towards systems that will impose greater accountability for posting links to unauthorized works. The EU’s directive makes clear that commercial hyperlinking to unauthorized content is indeed a communication to the public and therefor copyright infringement, while ensuring that the free flow of information through general public linking will not be threatened and the Internet will remain unbroken. It’s an approach that represents the greater goals of copyright law around the world, and other jurisdictions should follow the lead of the EU when crafting copyright policies that address the intricacies of the Internet.
 In a recent
In a recent 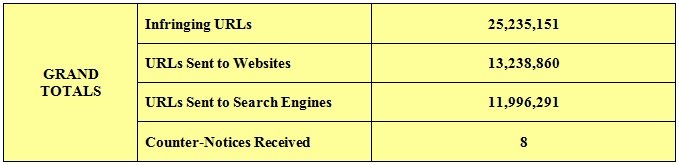
 With the Copyright Office undertaking a
With the Copyright Office undertaking a  Mason Law’s Arts & Entertainment Advocacy Clinic filed comments today with the U.S. Copyright Office detailing the frustrations and futilities experienced by everyday artists as they struggle with the DMCA system to protect their copyrights online.
Mason Law’s Arts & Entertainment Advocacy Clinic filed comments today with the U.S. Copyright Office detailing the frustrations and futilities experienced by everyday artists as they struggle with the DMCA system to protect their copyrights online. The U.S. Copyright Office is
The U.S. Copyright Office is