Cross-posted from the Mister Copyright blog.
 It should come as no surprise that popular websites make money by hosting advertisements. Anyone surfing the web has undoubtedly been bombarded with ads when visiting certain sites, and for websites that offer free services or user experiences, advertisements are often the only way to generate revenue. Unfortunately, websites that promote and distribute pirated material also attract advertisers to help fund their illicit enterprises, and despite a recent push for awareness and response to these sites, legitimate advertisers, search engines, and domain name registrars continue to enable them to profit from flagrant copyright infringement.
It should come as no surprise that popular websites make money by hosting advertisements. Anyone surfing the web has undoubtedly been bombarded with ads when visiting certain sites, and for websites that offer free services or user experiences, advertisements are often the only way to generate revenue. Unfortunately, websites that promote and distribute pirated material also attract advertisers to help fund their illicit enterprises, and despite a recent push for awareness and response to these sites, legitimate advertisers, search engines, and domain name registrars continue to enable them to profit from flagrant copyright infringement.
A 2014 study by the Digital Citizens Alliance found that ad-sponsored content theft is a big and growing business. Even after a year that saw the shutdown of some of the most notorious file-sharing websites, an examination of 589 illicit websites found aggregate annual advertising revenues of $209 million. Premium brand advertising also rose from 89 observed brands in 2013 to 132 to in 2014.
The transition from downloading to streaming as the preferred method of consuming entertainment has led to content thieves taking advantage of higher advertising rates, as the cost of advertising during a video stream is far greater than a traditional display ad. Additionally, the Digital Citizens Alliance stresses that websites are easily able to ditch a domain name targeted by authorities and set up shop under a new one, contributing to the never-ending whack-a-mole nature of online piracy:
The content theft industry’s low barriers to entry and the ability of operators to switch domains quickly make it easy for new sites to fill the void left by those that do get shut down, and to evade enforcement.
The presence of recognizable brand advertisements on websites involved in illegal activity does damage far beyond lining the pockets of those distributing the unauthorized works. When users visit a website in search of music, a television show, or movie, and they see the creative work (or links to the work) displayed alongside professional, recognizable advertisements, the advertisements lend legitimacy to the website. This can be especially dangerous for younger or less-informed users who have no idea that downloading or streaming the creative works through one of these websites is copyright infringement that will ultimately harm creators and artists.
The confusion these ad placements create is similar to the misperceptions furthered by search engines and domain name registrars that have made little effort to preclude pirate websites from taking advantage of their services. Despite promises to remove them from their search results, Google continues to display links to pirate websites alongside legitimate links in its results, often displaying the illicit links at the very top of the search results.
Filmmaker and artists’ rights activist Ellen Seidler recently exposed Google’s unwillingness to remove links to websites that distribute unauthorized creative works when she ran a simple Google search for her film And Then Came Lola. As she relates, not only was the film’s official website nowhere to be found among the first page of results, the list was made up of many websites offering pirated versions of the film. Sadly, most people searching for Ellen’s movie would not be able to immediately distinguish between legitimate and illicit links and would likely be steered towards a pirate website.
Domain name registrars have also added to the confusion surrounding the legitimacy of certain infamous pirate sites by allowing them to play domain name musical chairs and evade prosecution. The Pirate Bay—one of the most notorious file-sharing websites—has operated using domain names from 14 different countries, jumping from domain to domain name to stay online in the face of prosecution. Copyright Alliance CEO Keith Kupferschmid warns against providing sanctuary to sites like The Pirate Bay, revealing that the website recently returned to its original .org domain run by the U.S.-based Public Interest Registry (PIR):
It is shocking that a domain name registry in the United States – one that is dedicated to “the public interest” – is allowing a blatantly illegal site to have a home on the .org domain. This is especially disturbing given that the operators of The Pirate Bay have been found guilty of criminal copyright infringement, The Pirate Bay domain names have been seized or suspended around the globe, and even its co-founder, Peter Sunde, has walked away from it.
Despite these alarming trends in the facilitation of pirate websites, there have been some recent initiatives to deter companies from doing business with illicit websites. One notable initiative is the Trustworthy Accountability Group (TAG). A joint effort by the Association of National Advertisers (ANA), the American Association of Advertising Agencies (4A’s), and the Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB), TAG was formed “to create transparency in the business relationships and transactions that undergird the digital ad industry, while continuing to enable innovation.” In 2015, TAG announced the launch of the Brand Integrity Program Against Piracy—an effort to help advertisers and advertising agencies keep their ads off websites that promote or distribute counterfeit goods or pirated content.
TAG’s mission has resonated with both advertisers and ISPs, demonstrated by a recent announcement that dozens of leading ad agencies, as well as Google and GoDaddy, have taken TAG’s Anti-Piracy Pledge. The Pledge includes a vow to curb the placement of digital advertising on websites associated with the unauthorized distribution of materials and lists the following actions that companies can take to ensure compliance:
(i) directly employing the services of validated Digital Advertising Assurance Providers;
(ii) directly employing advertising placement services that carry the TAG logo “Certified Against Piracy”; and/or
(iii) placing online advertisements through Advertising Agencies that do business exclusively with advertising placement services that carry the TAG logo “Certified Against Piracy
TAG created Digital Advertising Assurance Providers (DAAPs) as part of its Brand Integrity Program to help advertisers identify and weed out websites that do not meet their brand standards. The DAAPs are validated technology companies that the advertisers can employ to gauge the level of risk they are comfortable with and then eliminate websites and other properties that do not meet the advertisers’ standards for risk of infringement.
It’s difficult to measure how harmful advertising on illicit websites is to creators and copyright owners, but it’s not a stretch to presume that without ad revenue, many pirate sites would lose their incentive to operate. In her call to action to marketers, Hannibal executive producer Martha De Laurentiis lays out the destructive effect piracy has on the creative community:
It forces companies to either shrink their production budgets or commit to fewer, less risky projects. And ultimately, it harms audiences by limiting the types of stories that creatives can tell.
De Laurentiis explains that these pirate sites bring in millions in advertising dollars a year, and because they don’t pay for distribution rights for the creative works they steal, profit margins are estimated at around 90%. Potential profits of this scale are irresistible to those behind the pirate sites, but with a little vigilance and responsibility these incentives could be eliminated.
The co-chairs of the International Creativity and Theft-Prevention Caucus, Senator Orrin Hatch, Senator Sheldon Whitehouse, Congressman Bob Goodlatte, and Congressman Adam Schiff, recently praised TAG for its promotion of the Anti-Piracy Pledge, and it seems like the movement for more responsibility in digital advertising is gaining traction. But domain name registrars and search engine services need to follow the example set by advertisers and establish accountability and awareness in their sectors. Only when these services refuse to aid websites that distribute stolen copyrighted works will real progress be made in the fight against digital piracy.
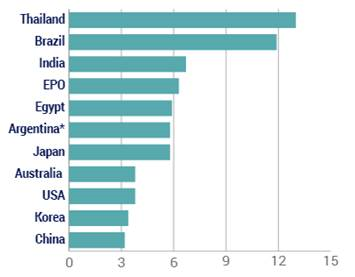
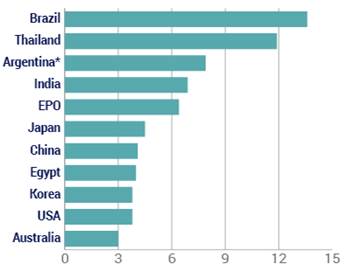
 Why are some of the biggest fights about patent policy almost pointless in some places? Because in many countries, including some of the world’s most important emerging economies, it takes so long to get patents that the rights have little meaning.
Why are some of the biggest fights about patent policy almost pointless in some places? Because in many countries, including some of the world’s most important emerging economies, it takes so long to get patents that the rights have little meaning.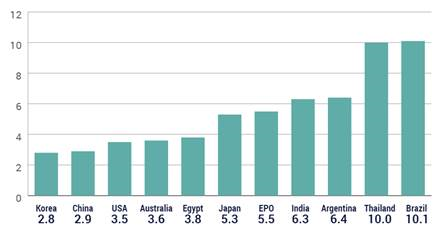

 It should come as no surprise that popular websites make money by hosting advertisements. Anyone surfing the web has undoubtedly been bombarded with ads when visiting certain sites, and for websites that offer free services or user experiences, advertisements are often the only way to generate revenue. Unfortunately, websites that promote and distribute pirated material also attract advertisers to help fund their illicit enterprises, and despite a recent push for awareness and response to these sites, legitimate advertisers, search engines, and domain name registrars continue to enable them to profit from flagrant copyright infringement.
It should come as no surprise that popular websites make money by hosting advertisements. Anyone surfing the web has undoubtedly been bombarded with ads when visiting certain sites, and for websites that offer free services or user experiences, advertisements are often the only way to generate revenue. Unfortunately, websites that promote and distribute pirated material also attract advertisers to help fund their illicit enterprises, and despite a recent push for awareness and response to these sites, legitimate advertisers, search engines, and domain name registrars continue to enable them to profit from flagrant copyright infringement.