By Mark Schultz and Devlin Hartline
The following essay is the first in a series of CPIP essays celebrating the 225th anniversary of the Copyright Act by recognizing the rich purposes, benefits, and contributions of copyright. This series of essays will be published together in a forthcoming collection entitled “Copyright’s Republic: Copyright for the Last and the Next 225 Years.”
The current academic and policy discussion of copyright focuses on balancing the gross economic benefits and harms of copyright. A more complete understanding of copyright can account for both the needs and rights of individuals and the public good. Copyright is important because it helps creators make an independent living and allows them to pursue and perfect their craft. In short, it enables a professional class of creators.
The creative industries benefit from this independence too. They must find a market, but they are not beholden to anybody but their customers and shareholders in choosing what creative works to promote. This enables a richly diverse cultural landscape, with movie studios, television channels, record labels, radio stations, and publishers specializing in vastly different types of material.
To understand the importance of a professional class of creators, it’s helpful to understand the paradoxical role of money in creativity. While some are quick to say, “It’s not about the money,” in some essential ways, it really is about the money. Certainly, for some creators, the proposition is straightforward. As the eighteenth-century poet Samuel Johnson famously and cynically proclaimed: “No man but a blockhead ever wrote, except for money.” For countless others, however, creative endeavors hardly bring riches. And even commercial creators frequently leave money on the table rather than do something they find distasteful. Nevertheless, money is important.
This seeming paradox can be resolved by considering the role of money overall in creative work. We can take creators at their word: There are many nonmonetary factors that influence and incentivize creativity, such as love, independence, curiosity, and passion. In fact, thinking about the money can hurt the creative process. But while creators may not “do it for the money,” the money is what makes it possible for them to spend their time honing skills and creating high-quality works. The money endows a professional class of creators and the various creative industries and channel partners that support them. This vibrant ecosystem – empowered by copyright – generates a rich diversity of cultural works.
Creative individuals, like every other human being, need to eat, and, like most of us, they need to work to eat. The real question is, what kind of work are they able to do? Some notable creators have worked in their spare time, but many of the greats thrive most when they can merge their avocation with their vocation. They get better at creating when their work is creation.
There is, of course, more than one way to fund professional creation – patronage, tenured university teaching, and commercial markets founded on copyright are notable ways to do it. One of the virtues of a commercial property rights system is that it fosters creative independence.
The independence afforded by a commercial system based on property rights is highlighted by contrasting it with the greater constraints under other systems. Before the first modern copyright statute passed nearly three centuries ago, many creators depended heavily on the patronage system. Wealthy patrons funded creative efforts by either commissioning works directly or employing creators to staff positions where they were given time to develop new works. To be sure, many great works were produced under this system – the musical compositions of Johann Sebastian Bach and Joseph Haydn stand testimony to this fact.
However, the economic benefits of patronage often came at the expense of the personal autonomy and integrity of these creators. As the old adage goes, “he who pays the piper calls the tune.” Sometimes these constraints were quite direct. When Johann Sebastian Bach attempted to leave the service of one of his patrons to go work for another, the former patron refused to accept his resignation and briefly had him arrested.
More important, patrons had tremendous say in the work of composers. They could decide what and when the composers wrote. They might not appreciate the value of the works created for them. For example, Bach’s Brandenburg Concertos are now recognized as works of genius. Unfortunately, the noble to whom they were dedicated, Christian Ludwig, the Margrave of Brandenburg, was apparently indifferent. The score sat on his shelf, unperformed and unappreciated, for decades. The concertos were not published until nearly 150 years later, after being rediscovered in an archive.
For these reasons, many composers dreamed of financial independence. For example, the composer Joseph Haydn once celebrated leaving behind the patronage of the Esterhazys, which was rather secure and relatively undemanding. Haydn moved to London, where he became the eighteenth-century equivalent of a successful rock star – in demand for his services and making lots of money. London had a private market – not yet so much supported by copyright and publishing as by private commissions and paid performances. In any event, Haydn prospered. In fact, at one point he wrote letters urging his friend Mozart to join him in London as soon as possible, unabashedly rhapsodizing over the money to be made there.
Still, he was now on his own, earning his own pay rather than being kept by a patron. For Haydn, artistic independence trumped economic security:
How sweet this bit of freedom really is! I had a kind Prince, but sometimes I was forced to be dependent on base souls. I often sighed for release, and now I have it in some measure. I appreciate the good sides of all this, too, though my mind is burdened with far more work. The realization that I am no bondservant makes ample amend for all my toils.
Haydn, Letter to Maria Anna von Genzinger, September 17, 1791
The modern copyright system, beginning with the English Statute of Anne in the early eighteenth century, freed creators from the restrictive patronage system. Like patronage, copyright offered creators the financial support they needed so that they could devote themselves to their craft. Unlike patronage, however, it gave them much-needed personal autonomy and artistic independence.
Beethoven, a young contemporary and student of Haydn working at the end of the patronage era, was able to support himself. His facility at performing his own difficult work helped him make a living. But he also used and supported copyright. He would often publish his works first in England to ensure that they received copyright there. He also lobbied the German states for a copyright law.
For Beethoven, too, money was important for the artistic independence it provided:
I do not aim at being a musical usurer, as you think, who composes only in order to get rich, by no means, but I love a life of independence and cannot achieve this without a little fortune, and then the honorarium must, like everything else that he undertakes, bring some honor to the artist.
Ludwig van Beethoven, Letter to publisher, August 21, 1810
The era of patronage was long ago, but human nature has not changed in the decades and centuries since. Creators still face the dilemma of trying to support themselves while maintaining independence. Every economic arrangement imposes some constraints, but some impose more than others.
A good example of how modern copyright enables individual creators to enjoy independence while supporting themselves is provided by the career of photographer Michael Stern. Stern is a hard-working creative entrepreneur – one 30-minute video he made required 103,937 photographs and 900 hours to produce. Stern doesn’t depend on subsidies or grants; rather, he values the independence he gets from being self-employed. He explains:
“The real benefit of being a self-employed photographer,” he says, “is that I can move through life on my terms and do what I want in the way I want to do it. That freedom drives me.” But, it’s not for everybody, he warns. “Nobody loves you like your mother, and even sometimes not even her. So ya gotta do it for yourself. If you don’t, you won’t have the drive needed to reach your goals.”
Instead of creating works that conform to the limited demands of their patrons, creators supply their works to the marketplace, where the demands of consumers are far more diverse. This proves beneficial to creators and society alike. Creators from all walks of life and with all sorts of interests can find the market that will support them, and this fosters a rich cultural landscape encompassing multiple political and social views.
Copyright fulfills its constitutional purpose of promoting progress by incentivizing creators through the grant of marketable rights to their works, but these rights do more than simply lure creators with the hope of economic benefits. Just as crucially, these rights endow creators with substantial personal autonomy while respecting their individuality and dignity. This fosters a creative environment conducive to the creation of high-quality works with enduring social value.
Copyright is a market-based system that supports a professional class of creators who rely on the value of their rights in order to make a living. These marketable rights have also given rise to entire creative industries that lend critical support to professional creators, and through the division of labor these industries enable professional creators to accomplish great feats that would be impossible if they worked alone.
The numbers testify to copyright’s success in helping to create a professional class of creators in the United States. As a recent report on the creative industries enabled by copyright found, there are 2.9 million people employed by over 700,000 businesses in the United States involved in the creation or distribution of the arts. They accounted for 3.9 percent of all businesses and 1.9 percent of all employees.
This creative ecosystem enables professional creators to produce the sorts of high-quality works that society values most. The popularity of these works in the marketplace makes them commercially valuable, and this in turn compensates professional creators and the creative industries that support them for creating the works that society finds so valuable.
This virtuous circle benefits creators and the public alike – just as the Framers had envisioned it. Copyright is not only doing its job, it is doing it well. The number of works available in the market is incredible – certainly more than anyone could ever possibly consume. And the diversity of voices able to connect with audiences in the marketplace makes our cultural lives all the more fulfilling.
 CPIP Founders Adam Mossoff & Mark Schultz filed an amicus brief today on behalf of 11 law professors in Converse v. International Trade Commission, a trademark case currently before the Federal Circuit.
CPIP Founders Adam Mossoff & Mark Schultz filed an amicus brief today on behalf of 11 law professors in Converse v. International Trade Commission, a trademark case currently before the Federal Circuit.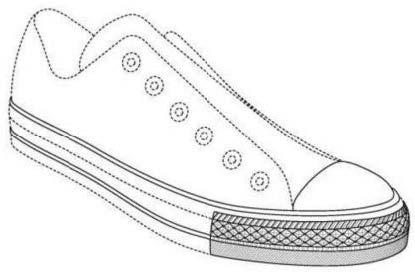
 This is the second in a series of posts summarizing CPIP’s 2016 Fall Conference, “Intellectual Property and Global Prosperity.” The Conference was held at Antonin Scalia Law School, George Mason University on October 6-7, 2016. Videos of the conference panels and keynote address, as well as other materials, are available on the
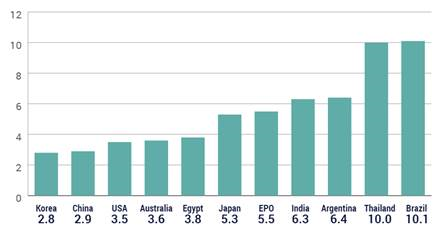
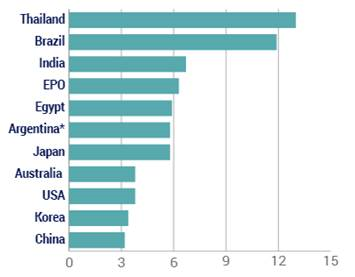
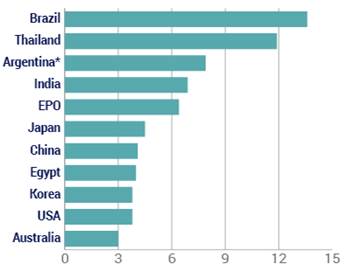
This is the second in a series of posts summarizing CPIP’s 2016 Fall Conference, “Intellectual Property and Global Prosperity.” The Conference was held at Antonin Scalia Law School, George Mason University on October 6-7, 2016. Videos of the conference panels and keynote address, as well as other materials, are available on the  Why are some of the biggest fights about patent policy almost pointless in some places? Because in many countries, including some of the world’s most important emerging economies, it takes so long to get patents that the rights have little meaning.
Why are some of the biggest fights about patent policy almost pointless in some places? Because in many countries, including some of the world’s most important emerging economies, it takes so long to get patents that the rights have little meaning.