This post is one of a series in the #Innovate4Health policy research initiative.
 By Nick Churchill
By Nick Churchill
Severe neonatal jaundice kills over 100,000 newborn babies annually and causes severe brain damage to thousands more. In most cases, the condition can be treated by simply shining a blue light on a baby’s skin. However, each year more than 6 million infants worldwide do not receive adequate treatment. The problem is particularly severe in low-income countries, where many hospitals cannot afford the equipment to treat jaundice.
To address this global health problem, the innovators at D-Rev, a non-profit firm based in San Francisco, designed a high-performance, affordable device called Brilliance to treat severe neonatal jaundice. Brilliance has been praised by users as “effective and user-friendly,” and it was honored as the top innovation in the Health category of the 2016 Tech Awards. Since the introduction of the first Brilliance model in 2012, D-Rev estimates that the device has treated over 250,000 babies and has averted approximately 3,400 infant deaths and disabilities.
Neonatal jaundice occurs when a newborn has elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood. Approximately 18% of babies have severely high levels of bilirubin, which, left untreated, can lead to brain damage, cerebral palsy, hearing loss, and even death. Severe jaundice can be treated with a process called phototherapy, which involves placing the baby under special blue lights. When the light is absorbed by the infant’s skin, it helps break down bilirubin. Treated properly, severe jaundice usually does not cause lasting damage.
Phototherapy has long been recognized as a simple and effective treatment for severe neonatal jaundice; but at around $3,000, traditional phototherapy devices are prohibitively expensive for many hospitals in developing countries. Hospitals that can obtain a traditional unit are often unable to afford the maintenance and repair costs necessary to keep it running. The unreliable electrical systems in many developing countries can cause voltage spikes that damage device components. Commonly used fluorescent lamps require frequent replacement. As a result, phototherapy is unavailable to babies in many developing communities.
D-Rev is a product development company founded in 2007 to provide world-class, affordable healthcare technologies to people living on very low incomes. After learning that severe jaundice continues to cause brain damage in many parts of the world, D-Rev staff members visited hospitals in India and Nigeria to assess the availability of effective phototherapy and found that most of these hospitals did not have phototherapy devices that met standards for care. With the problem identified, D-Rev’s design team got to work.
D-Rev’s advanced devices, for which they are seeking a patent, uses LEDs that last 60x longer than fluorescent lamps, saving hospitals over $240 per year on replacement bulbs. Brilliance is designed to withstand a range of power fluctuations without affecting performance and operates without cooling fans or filters, so there are fewer parts to maintain. The device is height-adjustable and can be integrated with the wide variety of other critical neonatal medical equipment found in hospitals serving low-income communities.
Importantly, D-Rev’s devices are inexpensive to manufacture, which allows D-Rev to sell them for hundreds, instead of thousands, of dollars. The newest model incorporates the technology in their patent application, which ensures light intensity levels remain consistent across the treatment area at any angle of tilt. D-Rev also developed an integrated light meter to help healthcare providers ensure that infants receive appropriate doses of light, something many low income hospitals were previously unable to do. Thus, the innovations developed by D-Rev are improving the technology and reducing cost, making much needed treatments more accessible in the developing world.
After successfully designing an affordable and effective phototherapy device, D-Rev’s next challenge was to find a way to deliver Brilliance to the hospitals that needed it most. D-Rev’s CEO, Krista Donaldson, recognized that the firm would need help to establish a sales and distribution network, noting, “We knew we needed to license in this case.” To achieve its goals, D-Rev needed to find a partner willing to manufacture its products and distribute them to hospitals and clinics in the poorest communities in the world.
D-Rev licensed its technology to Phoenix Medical Systems, a neonatal equipment firm based in India, who agreed to manufacture and distribute Brilliance while capping its price. The licensing agreement was structured so that D-Rev would take a smaller royalty on sales to public and district hospitals, which tend to serve lower-income patients. In this way, D-Rev used its intellectual property rights to align the incentives of Phoenix’s sales team with D-Rev’s goal of reaching those patients who are most in need of affordable phototherapy.
Donaldson has explained why D-Rev’s protection of its intellectual property “is a prerequisite to having the broadest possible impact.” First, intellectual property rights allow D-Rev to ensure that the quality of its products remains consistent. As Donaldson notes, a medical device “cannot fail the user, particularly a user in a vulnerable population.” Second, inconsistency erodes consumer trust, which limits the impact of a product. Third, D-Rev recognizes that designing an effective product does not necessarily solve the targeted problem. By retaining control of its intellectual property, D-Rev can ensure consistent manufacturing of its products, sustainable delivery to users who need it, and continued maintenance and support. Finally, D-Rev protects its intellectual property because the market is “the most economically sustainable and scalable way” of reaching their intended customers.
D-Rev has demonstrated that the value of intellectual property goes beyond incentivizing life-saving innovation like Brilliance. Intellectual property rights empower innovators to increase their impact by partnering with market leaders like Phoenix. As Donaldson concluded: “To succeed, serious partners (for-profit or non-profit) must also make an investment, and none are willing to do that with the threat of knock-offs.”
#Innovate4Health is a joint research project by the Center for the Protection of Intellectual Property (CPIP) and the Information Technology & Innovation Foundation (ITIF). This project highlights how intellectual property-driven innovation can address global health challenges. If you have questions, comments, or a suggestion for a story we should highlight, we’d love to hear from you. Please contact Devlin Hartline at jhartli2@gmu.edu.
 CPIP co-founder
CPIP co-founder  Unfortunately, much of the discussion centered around a perceived problem with patent “trolls.” This
Unfortunately, much of the discussion centered around a perceived problem with patent “trolls.” This  By Mandi Hart
By Mandi Hart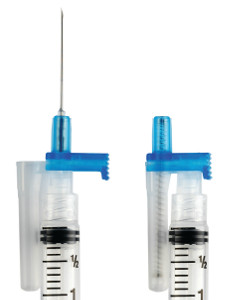 Thomas J. Shaw, founder of Retractable Technologies, created a technological solution to the problem after seeing a television report of a doctor who contracted HIV from an accidental needlestick. He designed a single use spring-loaded syringe that immediately pulls the needle back inside the just-used syringe. Thus, the needle is automatically covered and incapable of harming anyone.
Thomas J. Shaw, founder of Retractable Technologies, created a technological solution to the problem after seeing a television report of a doctor who contracted HIV from an accidental needlestick. He designed a single use spring-loaded syringe that immediately pulls the needle back inside the just-used syringe. Thus, the needle is automatically covered and incapable of harming anyone. From these initial tests, Shaw founded Retractable Technologies, and the value of his innovation was immediately recognized. He received
From these initial tests, Shaw founded Retractable Technologies, and the value of his innovation was immediately recognized. He received 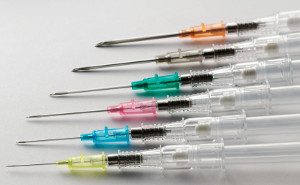 The value of the retractable syringe design has been important to advancing health care goals worldwide. The World Health Organization has recognized the
The value of the retractable syringe design has been important to advancing health care goals worldwide. The World Health Organization has recognized the  It seems no matter how many times the mole gets whacked, it keeps popping back up. The latest incarnation of this problem is a recent
It seems no matter how many times the mole gets whacked, it keeps popping back up. The latest incarnation of this problem is a recent  On February 16, 2017, CPIP hosted a panel discussion,
On February 16, 2017, CPIP hosted a panel discussion,  In 2007, Ghanaian tech entrepreneur
In 2007, Ghanaian tech entrepreneur  Through the combination of EarlySensor and Goldkeys, mPedigree’s innovative technology is facilitating the protection of both brand owners and consumers and ensuring that data collection and authentication mechanisms are leading to the safer distribution of medicines, cosmetics, seeds, and other essential products.
Through the combination of EarlySensor and Goldkeys, mPedigree’s innovative technology is facilitating the protection of both brand owners and consumers and ensuring that data collection and authentication mechanisms are leading to the safer distribution of medicines, cosmetics, seeds, and other essential products. By providing a dynamic link between consumers and manufacturers, mPedigree is making communications at the point of purchase routine and creating value for consumers, manufacturers, regulatory agencies, and sellers. A project ten years in the making, mPedigree is built on the recognition that protecting intellectual property—both mPedigree’s and its clients—can save lives.
By providing a dynamic link between consumers and manufacturers, mPedigree is making communications at the point of purchase routine and creating value for consumers, manufacturers, regulatory agencies, and sellers. A project ten years in the making, mPedigree is built on the recognition that protecting intellectual property—both mPedigree’s and its clients—can save lives. One promising example of these new mobile diagnostic applications for eye care is the
One promising example of these new mobile diagnostic applications for eye care is the  How does PEEK work? An app and a clip-on adapter
How does PEEK work? An app and a clip-on adapter  This is the second in a series of posts summarizing CPIP’s 2016 Fall Conference, “Intellectual Property and Global Prosperity.” The Conference was held at Antonin Scalia Law School, George Mason University on October 6-7, 2016. Videos of the conference panels and keynote address, as well as other materials, are available on the
This is the second in a series of posts summarizing CPIP’s 2016 Fall Conference, “Intellectual Property and Global Prosperity.” The Conference was held at Antonin Scalia Law School, George Mason University on October 6-7, 2016. Videos of the conference panels and keynote address, as well as other materials, are available on the