 Innovation is all around us. We love and appreciate the latest video games, software apps, and smartphones. We await the integration of self-driving cars and other forms of artificial intelligence. Beyond the gadgets and luxuries we think we can’t live without, there are even more essential products that affect the lives of millions around the world on a daily basis. Patented medicines are at the top of the list of innovations that save lives and preserve the quality of life. Unfortunately, some proposed changes to European patent law are jeopardizing the development and delivery of safe and effective drugs, threatening jobs and innovation, and putting global public health at risk.
Innovation is all around us. We love and appreciate the latest video games, software apps, and smartphones. We await the integration of self-driving cars and other forms of artificial intelligence. Beyond the gadgets and luxuries we think we can’t live without, there are even more essential products that affect the lives of millions around the world on a daily basis. Patented medicines are at the top of the list of innovations that save lives and preserve the quality of life. Unfortunately, some proposed changes to European patent law are jeopardizing the development and delivery of safe and effective drugs, threatening jobs and innovation, and putting global public health at risk.
Policy-makers and the public acknowledge that balance is critical in the legal regimes governing essential medicines. Our generation is the beneficiary of patent protections which strike a balance. European regulators have long acknowledged that the benefits of new cures (e.g., arising from the research and development of therapies) require a societal investment in the form of intensive capital resources and strong intellectual property protection. In turn, a balanced system includes a reasonable patent term as a quid pro quo for the public disclosure of knowledge and the follow-on generic industry.
The medicines sector highlights the need for that careful balance, as well as the success of the current legal regime. New drug research and the development of new cures is extremely capital intensive. Legions of European scientists, engineers, and clinicians can work for years on a new drug’s development and regulatory review. A recent Tufts University center study reports that, on average, more than $2.6 billion is spent on R&D for a new prescription drug that gains market approval; the life-cycle cost rises to $2.9 billion when other post-approval development costs are included.[1] This is a 145% increase, correcting for inflation, over the estimate the center made in 2003.
In practice, for every drug that is successfully developed, reviewed, and made available to patients, many dozens more fail. CPIP Senior Scholar Erika Lietzan has observed:
The overall attrition rate for new drugs remains high—‘horrendously high’ according to [U.S.] NIH Director Francis Collins—and may be increasing. Recent estimates place the phase 2 failure rate at sixty-five to seventy percent and even higher for drugs with new mechanisms of action.[2]
Due to this high failure rate and costly investment in R&D, well-balanced intellectual property rights are essential for innovators to commercialize the products that do make it to market and improve—or even save—consumers’ lives.
Medicines must be safe and effective, and while regulatory review is essential, it is a time-consuming and highly expensive process. The reality is that the essential patent term is eaten away by years of regulatory review delay.[3] This extra review process is what makes the investment and research questions in the bio-pharmaceutical space so different from a smartphone or the latest virtual reality entertainment software. Professor Lietzan christened this the “innovation paradox.” She explains:
In medicine today, we face an innovation paradox. Companies that develop new medicines depend on a period of exclusive marketing after approval, to fund their research and development programs. This period is made possible by patent protection and regulatory data exclusivity.[4]
Likewise, it is the reason that there needs to be some supplementary legal protection to raise new capital and investments for cures and therapies.
The practical effect is that the necessary regulatory review results in the loss of years of effective patent term protection, warranting special treatment for innovative pharmaceutical products that come to market with little time to realize the benefits of exclusivity. In the 1990s, European policy-makers successfully restored the balance between innovation and the public interest by establishing the Supplementary Protection Certificate (SPC), which provides limited exclusive legal protection after a patent’s expiry.
Supplemental Protection Certificates Ensure a Necessary Balance
Supplementary Protection Certificates (SPCs) reinforce the balance between the rights of innovators and the public by extending the exclusive term for a variety of compounds, e.g., human and veterinary medicines and plant products. SPCs provide a limited extension of legal protections (e.g., exclusivity capped at five-and-one-half years) to compensate for the patent term effectively lost during the regulatory review process to ensure safety and efficacy.
Since SPCs were established, it is estimated that more than 20,000 SPCs for patented products have been filed in Europe during the period 1991–2016.[5] Despite the SPC’s twenty-plus-year track record of success, it, and the balance it preserves, is coming under pressure due to special interest lobbying by the generic drug industry.
The European Commission (EC) recently proposed waiving the SPC for pharmaceuticals and biosimilars[6] and permitting limited generic drug protection via the following two provisions prior to the SPC’s expiration:
(1) The “Manufacturing Provision.” This proposal would “allow EU generic or biosimilar manufacturers to develop and store generic or biosimilar manufacturers in Europe . . . with the goal of enabling immediate generic or biosimilar market entry following the expiration of intellectual property protections . . . .”
(2) The “Export Provision.” This proposal would “allow generic or biosimilar manufacturers to export products to countries where no intellectual property protection for the products is in place.”
While these two proposals are touted as limited in scope, their impact would be significant and detrimental on many fronts across Europe, including for the public health, innovation, jobs, and trade.
The Dangerous Impact of SPC Waiver
The overall impact of the SPC waiver threatens the balance that has worked so well for twenty-plus years, plain and simple. Specifically, the negative impact and risks are evidenced through the inherent complexity of a medicine’s regulatory review process, undermining the public health via counterfeit medicines, and harming Europe’s economy and jobs.
a. Risks of Limiting Innovation for a Variety of Important New Compounds and Cures
The most important reason to preserve the current balance is that it is a proven path to develop new medicines for the public’s health. Recently, a commentator highlighted two critical medicines that would not be available to patients, but for the opportunity afforded by the SPC process: (1) Fingolimod (a drug to treat renal failure after a kidney transplant that was subsequently brought to the market for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS)); and, (2) Secukinumab (a treatment of psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis (a type of spinal arthritis) that required an extended, more complicated clinical trial review period).[7] In both cases, the benefits of the additional period of exclusivity under the SPC provided the necessary time and resources for the follow-on clinical trials and research for the medicine’s safety and efficacy review.
Ultimately, SPCs benefit capital intensive pursuits, such as new drug discovery and development, by yielding new drugs or new applications for such drugs. More importantly, the patients who need these drugs clearly benefit. As Europe looks to an aging population and increasing health care costs, there is an ever growing need for effective cures for diseases such as HIV/AIDS, Alzheimer’s, multiple sclerosis (MS), cancers, and others requiring orphan drugs.[8] The SPC system is an important part of how the next generation of pioneering life-saving medicines will come into being.
b. Risk to the Public Health and Safety Through Counterfeit Medicines
Another key concern for stakeholders and the public at-large resulting from the current proposals is the inevitable increase of piracy and counterfeiting of these medicines. Global piracy and counterfeiting of medicines is big business. A 2016 study estimated that drug piracy costs Europe more than €10 billion each year, may result in the loss of up to 40,000 direct jobs, and may have a total direct and indirect negative impact of over €17 billion and 90,000 job losses.[9]
In addition to the significant financial impact, piracy and counterfeiting is a matter of public health and safety. It is often the case that the counterfeit medicines are manufactured without sufficient quality controls, or worse, with unsafe or dangerous substitute ingredients. The SPC Export Provision waiver heightens the risk that poor quality or unsafe counterfeits will be diverted across borders. Counterfeit drugs are a massive public health risk throughout Europe and big business for criminal enterprises that either ship fake, unsafe medicine or divert counterfeits across borders trying to profit on the product demand and price differentials among nations.
The SPC Export Provision waiver will ultimately increase medicines piracy and counterfeiting on many grounds, including making it difficult to distinguish between medicines produced legally in one country and other jurisdictions without adequate IP protection, making it difficult to prevent product diversion, and diminishing quality control due to infringement.
c. The European Economic Case: Jobs and Trade
Europe boasts a first-class research-based pharmaceutical industry which is estimated to have invested €31.5 billion in R&D in 2015 alone.[10] The leading European countries which contribute to this annual R&D investment include Germany, France, Italy, Spain, and the U.K. The research industry trade association, EFPIA, explains some of the economic benefits of the SPC regime:
The SPC is part of an incentives framework that helps to generate the 35 billion in investment in R&D in Europe by the research-based industry. . . . It helps to safeguard over 750,000 jobs directly employed by biopharmaceutical companies and critically facilitates, research into unmet medical needs, finding treatments and cures for patients across Europe and beyond.[11]
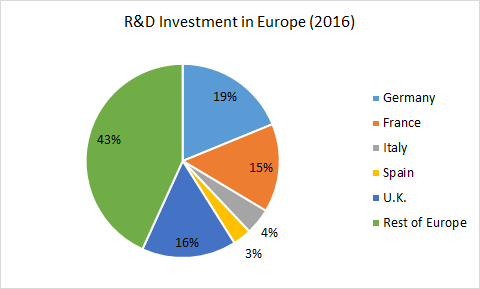
European Pharmaceutical Industry: Recent Trends and Statistics[12]
Evaluating the economic factors around an industrial policy proposal—new manufactured units, SMEs, direct and indirect jobs—is a legitimate part of the policy debate. In the public health context, it is one of several factors for policy-makers. Both sides of the debate have offered competing economic analyses of the impact of the waiver.[13] However, the past is prologue, and Europe has 20-plus years of a positive economic experience with the SPC regime.
Today’s debate over the SPC waiver is reminiscent to biotechnology patentability debates in the 1980s that weakened intellectual property rights and drove innovative activity out of Europe. As a recent article explains, the legal choices made by Europe during that crucial era led to an irreparable loss of its technological global leadership in the biotech and health care arena:
Europe lost the competitive and commercial edge in biotechnology to the U.S., which had the foresight to protect a new and innovative industry. This new industry both revolutionized modern medical research and healthcare treatments and brought economic growth to the many U.S. cities in which these new companies sprouted and flourished.[14]
Likewise, additional commentators warn that an SPC waiver poses a threat to Europe’s global competiveness: “Europe is becoming an innovation backwater, easily outspent on R&D by peer nations such as the United States, Japan, South Korea and Australia, according to the 2017 European Innovation Scorecard.”[15] While there are allegations that the SPC waiver would be beneficial for European jobs and its economy, this has been debunked for their flawed methodology or extreme overstatement of the facts.[16]
Conclusion
The EC’s proposed SPC waiver provisions are a cure far worse than the disease. The policy debate around this subject boils down to whether Europe wants a strong or a weak health care system for its citizens. The purported goals advanced by special interest tactics certainly sound noble: more competition, lower prices. In fact, the opposite ignoble result is an inevitable undermining of the incentives for the discovery and development new medicines.
The EC should reconsider the proposed waiver for many reasons. The current SPC system offers a successful twenty-year-plus track record. It respects the balance between patients and the medicines innovation ecosystem. The waiver will directly stifle innovation in the guise of fostering competition, as well as dampen the future of innovative medicines and harm the European economy. One must conclude that the SPC waiver should be reconsidered for the sake of the public health and future well-being of the European citizenry.
[1] https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/cost-to-develop-new-pharmaceutical-drug-now-exceeds-2-5b/.
[2] Erika Lietzan, The Drug Innovation Paradox, 83 Missouri Law Review 39 at 78-79 (2018) (describing the U.S. regime), available at https://ssrn.com/abstract=2948604.
[3] Id. at 59 (“Through the 1970s, as the modern new drug premarket paradigm took shape, scholars and policymakers became aware of diminishing effective patent life. Because inventors typically file active ingredient patent applications before clinical testing starts, these patents tend to issue before or during the trials. At the time, a patent lasted for seventeen years from issuance. Today, it generally lasts for twenty years from the filing of the patent application. In either case, a significant portion of the term of an active ingredient patent may lapse before FDA approves the marketing application. This shortens the period of time that the drug sponsor may exploit the invention in the market while enjoying patent rights.”).
[4] Id.
[5] Malwina Mejer, 25 years of SPC protection for medicinal products in Europe: Insights and challenges (May 2017), available at https://ec.europa.eu/info/publications/25-years-spc-protection-medicinal-products-europe-insights-and-challenges_en.
[6] The European Medicines Agency (EMA) explains that “[a] biosimilar is a biological medicine highly similar to another already approved biological medicine (the ‘reference medicine’). Biosimilars are approved according to the same standards of pharmaceutical quality, safety and efficacy that apply to all biological medicines. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is responsible for evaluating the majority of applications to market biosimilars in the European Union (EU). Biological medicines offer treatment options for patients with chronic and often disabling conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune disease and cancers.” Available at https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/overview/biosimilar-medicines-overview.
[7] Nathalie Moll, Betting on innovation, the case for the SPC, available at https://www.efpia.eu/news-events/the-efpia-view/blog-articles/betting-on-innovation-the-case-for-the-spc/.
[8] The European Medicines Agency (EMA) notes that “[a]bout 30 million people living in the European Union (EU) suffer from a rare disease. The [EMA] plays a central role in facilitating the development and authorization of medicines for rare diseases, which are termed ‘orphan medicines’ in the medical world.” Available at https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/overview/orphan-designation.
[9] http://www.pharmexec.com/counterfeit-drugs-cost-europe-more-10-billion-year.
[10] https://www.ihealthcareanalyst.com/european-pharmaceutical-industry-recent-trends-statistics/.
[11] https://efpia.eu/news-events/the-efpia-view/statements-press-releases/efpia-statement-on-the-implementation-of-the-spc-manufacturing-waiver/.
[12] https://www.ihealthcareanalyst.com/european-pharmaceutical-industry-recent-trends-statistics/.
[13] http://ecipe.org/blog/ec-spc/; https://www.medicinesforeurope.com/newsroom/.
[14] Kevin Madigan & Adam Mossoff, Turning Gold Into Lead: How Patent Eligibility Doctrine is Undermining U.S. Leadership in Innovation, 24 Geo. Mason L. Rev. 939 (2017) (“We believe these are sensible provisions to avoid weakening Europe’s IP framework further, particularly in today’s context of intense global competition for pharmaceutical research and development investment.”), available https://ssrn.com/abstract=2943431.
[15] See, e.g., Philip Stevens, The European Commission’s pharmaceutical innovation incentives review is at risk of serious overreach, available at http://ecipe.org/blog/ec-spc/.
[16] Sussell et al, Reconsidering the economic impact of the EU manufacturing and export provisions, J. of Generic Medicines, 1-17. (citing arithmetic error and providing a counter factual analysis of the unit, job, SME, and economic benefits in a recent generic industry study praising the SPC waiver proposal).
 In a new CPIP policy brief entitled The End of Patent Groupthink, CPIP Senior Fellow for Innovation Policy Jonathan Barnett highlights some cracks that have emerged in the recent policy consensus that the U.S. patent system is “broken” and it is necessary to “fix” it. Policymakers have long operated on the basis of mostly unquestioned assumptions about the supposed explosion of low quality patents and the concomitant patent litigation that purportedly threaten the foundation of the innovation ecosystem. These assumptions have led to real-world policy actions that have weakened patent rights. But as Prof. Barnett discusses in the policy brief, that “groupthink” is now eroding as empirical evidence shows that the rhetoric doesn’t quite match up to the reality. This has translated into incremental but significant movements away from the patent-skeptical trajectory that has prevailed at the Supreme Court, the USPTO, and the federal antitrust agencies.
In a new CPIP policy brief entitled The End of Patent Groupthink, CPIP Senior Fellow for Innovation Policy Jonathan Barnett highlights some cracks that have emerged in the recent policy consensus that the U.S. patent system is “broken” and it is necessary to “fix” it. Policymakers have long operated on the basis of mostly unquestioned assumptions about the supposed explosion of low quality patents and the concomitant patent litigation that purportedly threaten the foundation of the innovation ecosystem. These assumptions have led to real-world policy actions that have weakened patent rights. But as Prof. Barnett discusses in the policy brief, that “groupthink” is now eroding as empirical evidence shows that the rhetoric doesn’t quite match up to the reality. This has translated into incremental but significant movements away from the patent-skeptical trajectory that has prevailed at the Supreme Court, the USPTO, and the federal antitrust agencies. We “stand on the shoulder of giants,” goes the famous adage. In a groundbreaking new law review article,
We “stand on the shoulder of giants,” goes the famous adage. In a groundbreaking new law review article,  Innovation is all around us. We love and appreciate the latest video games, software apps, and smartphones. We await the integration of self-driving cars and other forms of artificial intelligence. Beyond the gadgets and luxuries we think we can’t live without, there are even more essential products that affect the lives of millions around the world on a daily basis. Patented medicines are at the top of the list of innovations that save lives and preserve the quality of life. Unfortunately, some proposed changes to European patent law are jeopardizing the development and delivery of safe and effective drugs, threatening jobs and innovation, and putting global public health at risk.
Innovation is all around us. We love and appreciate the latest video games, software apps, and smartphones. We await the integration of self-driving cars and other forms of artificial intelligence. Beyond the gadgets and luxuries we think we can’t live without, there are even more essential products that affect the lives of millions around the world on a daily basis. Patented medicines are at the top of the list of innovations that save lives and preserve the quality of life. Unfortunately, some proposed changes to European patent law are jeopardizing the development and delivery of safe and effective drugs, threatening jobs and innovation, and putting global public health at risk.
 By
By  It is undeniable that the patent system has been
It is undeniable that the patent system has been  Poor sanitation poses an ongoing threat to the health and well-being of people in the developing world. Severe health problems, death, and disease can be directly linked to unsafe hygiene practices that continue to plague many countries. A
Poor sanitation poses an ongoing threat to the health and well-being of people in the developing world. Severe health problems, death, and disease can be directly linked to unsafe hygiene practices that continue to plague many countries. A  In 2012, with
In 2012, with  Access to proper sanitation and clean water is vital for the
Access to proper sanitation and clean water is vital for the  Invented by Jim McHale, Daigo Ishiyama and Greg Gatarz, the
Invented by Jim McHale, Daigo Ishiyama and Greg Gatarz, the  Crucially, the design of the pan allows for potential variations according to local customs and demands, such as using the facilities by squatting or sitting or adapting to the shape of the pit for the latrine. The core concept around which the pan is based is the counterweighted “flapper” itself. The counterweight is specifically set so that the flap remains closed until the additional force of water – not just the waste itself – is poured into the pan. The pour-flush mechanic also creates a liquid seal, with a minimal amount of water remaining on top of the flap after use to help ensure prevention of transmission of insects or gases. This approach, utilizing a basic mechanism while leaving room for responsive adjustments in design, allows the SaTo pan to be adapted globally while maintaining a simple but effective means of providing basic health benefits.
Crucially, the design of the pan allows for potential variations according to local customs and demands, such as using the facilities by squatting or sitting or adapting to the shape of the pit for the latrine. The core concept around which the pan is based is the counterweighted “flapper” itself. The counterweight is specifically set so that the flap remains closed until the additional force of water – not just the waste itself – is poured into the pan. The pour-flush mechanic also creates a liquid seal, with a minimal amount of water remaining on top of the flap after use to help ensure prevention of transmission of insects or gases. This approach, utilizing a basic mechanism while leaving room for responsive adjustments in design, allows the SaTo pan to be adapted globally while maintaining a simple but effective means of providing basic health benefits. By Alex Summerton & Nick Churchill
By Alex Summerton & Nick Churchill One solution to these problems is to effectively move clinics to the patients through
One solution to these problems is to effectively move clinics to the patients through  Daktari (Swahili for “Doctor”) Diagnostics is working on the development of a point-of-care testing platform that meets the ASSURED standards. Daktari’s portable point-of-care platform,
Daktari (Swahili for “Doctor”) Diagnostics is working on the development of a point-of-care testing platform that meets the ASSURED standards. Daktari’s portable point-of-care platform,  Earlier this month, a bipartisan group of Senators introduced the Creating and Restoring Equal Access to Equivalent Samples Act (or
Earlier this month, a bipartisan group of Senators introduced the Creating and Restoring Equal Access to Equivalent Samples Act (or  Advocates for changing the patent venue rules, which dictate where patent owners can sue alleged infringers, have been arguing that their remedy will cure the supposed disease of abusive “trolls” filing suit after suit in the Eastern District of Texas. This is certainly true, but it’s only true in the sense that cyanide cures the common cold. What these advocates don’t mention is that their proposed changes will weaken patent rights across the board by severely limiting where all patent owners—even honest patentees that no one thinks are “trolls”—can sue for infringement. Instead of acknowledging the broad collateral damage their changes would cause to all patent owners, venue revision advocates invoke the talismanic “troll” narrative and hope that nobody will look closely at the details. The problem with their take on venue revision is that it’s neither fair nor balanced, and it continues the disheartening trend of equating “reform” with taking more sticks out every patent owner’s bundle of rights.
Advocates for changing the patent venue rules, which dictate where patent owners can sue alleged infringers, have been arguing that their remedy will cure the supposed disease of abusive “trolls” filing suit after suit in the Eastern District of Texas. This is certainly true, but it’s only true in the sense that cyanide cures the common cold. What these advocates don’t mention is that their proposed changes will weaken patent rights across the board by severely limiting where all patent owners—even honest patentees that no one thinks are “trolls”—can sue for infringement. Instead of acknowledging the broad collateral damage their changes would cause to all patent owners, venue revision advocates invoke the talismanic “troll” narrative and hope that nobody will look closely at the details. The problem with their take on venue revision is that it’s neither fair nor balanced, and it continues the disheartening trend of equating “reform” with taking more sticks out every patent owner’s bundle of rights.