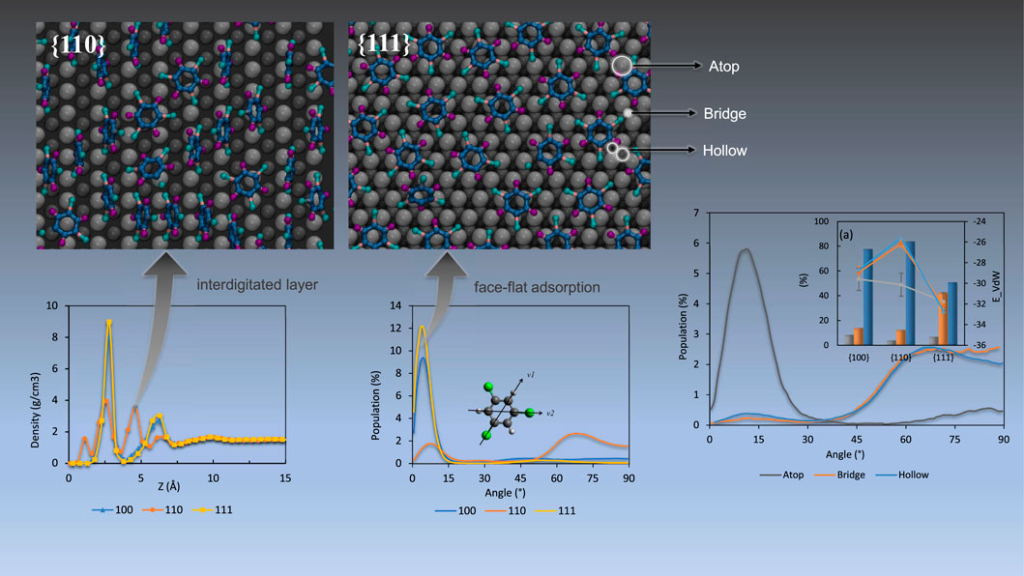
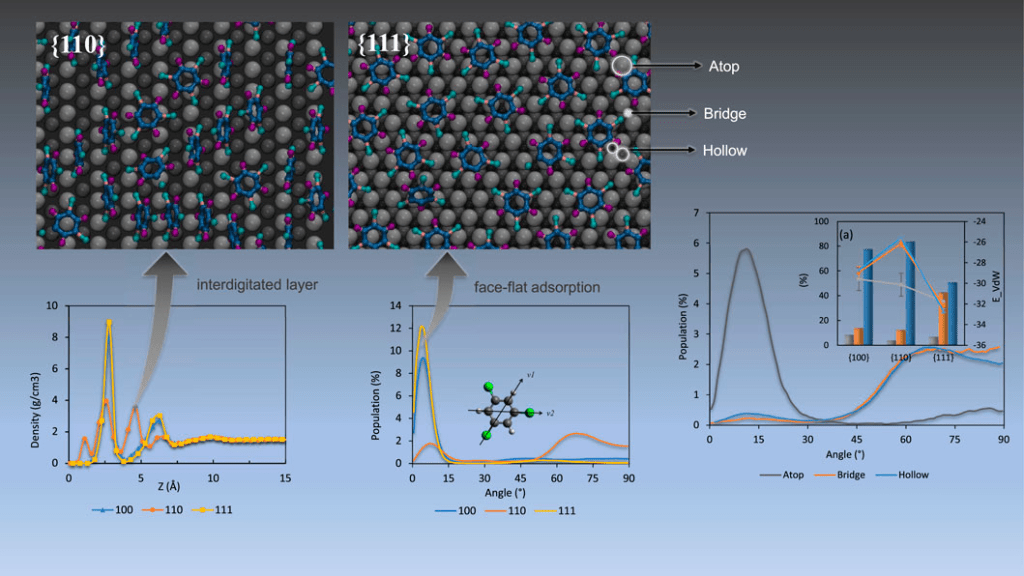
The present work quantifies metal-contaminant interactions between palladium substrates and three salient chlorinated organic contaminants, namely trichloroethylene 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene (TCB), and 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl (PCB77). Given that Pd is one of the conventional catalytically active materials known for contaminant removal, maximizing catalytic efficiency through optimal adsorption dynamics reduces the cost of remediation of contaminants that are persistent water pollutants chronically affecting public health. Adsorption efficiency analyses from all-atom molecular dynamics (MD) simulations advance the understanding of reaction mechanisms available from density functional theory (DFT) calculations to an extractable feature scale that can fit the parametric design of supported metal catalytic systems and feed into high throughput catalyst selection. Data on residence time, site-specific adsorption, binding energies, packing geometries, orientation profiles, and the effect of adsorbate size show the anomalous behaviour of organic contaminant adsorption on the undercoordinated {110} surface as compared to the {111} and {100} surfaces. The intermolecular interaction within contaminants from molecular dynamics simulation exhibits refreshing results than ordinary single molecule density functional theory calculation. Since complete adsorption and dechlorination is an essential step for chlorinated organic contaminant remediation pathways, the presented profiles provide essential information for designing efficient remediation systems through facet-controlled palladium nanoparticles. The research was conducted by Hao Guo, Emily A. Gerstein, Kshitij C.Jha, Iskinder Arsano, M.Ali Haider, and Tuhin S.Khan.

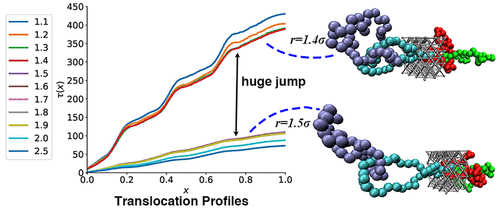
The translocation of polymers through pores and channels is an archetypal process in biology and is widely studied and exploited for applications in bio- and nanotechnology. In recent times, the translocation of polymers of various different topologies has been studied both experimentally and by computer simulation. However, in some cases, a clear understanding of the precise mechanisms that drive their translocation dynamics can be challenging to derive. Experimental methods are able to provide statistical details of polymer translocation, but computer simulations are uniquely placed to uncover a finer level of mechanistic understanding. In this work, we use high-throughput molecular simulations to reveal the importance that knot insertion rates play in controlling translocation dynamics in the small pore limit, where unexpected nonpower law behavior emerges. This work both provides new predictive understanding of polycatenane translocation and shows the importance of carefully considering the role of the definition of translocation itself. The research was conducted by Zifeng Wang and Robert M. Ziolek.

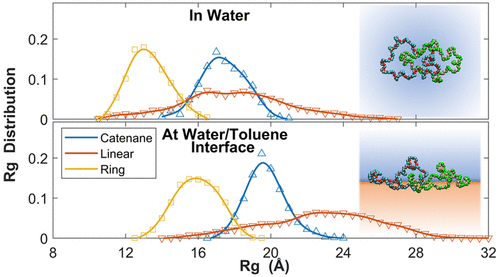
In recent decades, advances in the syntheses of mechanically interlocked macromolecules, such as catenanes, have led to much greater interest in the applications of these complexes, from molecular motors and actuators to nanoscale computational memory and nanoswitches. Much remains to be understood, however, regarding how catenated ring compounds behave as a result of the effects of different solvents as well as the effects of solvent/solvent interfaces. In this work, we have investigated, using molecular dynamics simulations, the effects of solvation of poly(ethylene oxide) chains of different topologies─linear, ring, and [2]catenane─in two solvents both considered favorable toward PEO (water, toluene) and at the water/toluene interface. Compared to ring and [2]catenane molecules, the linear PEO chain showed the largest increase in size at the water/toluene interface compared to bulk water or bulk toluene. Perhaps surprisingly, observations indicate that the tendency of all three topologies to extend at the water/toluene interface may have more to do with screening the interaction between the two solvents than with optimizing specific solvent–polymer contacts. The research was conducted by Saeed Akbari Shandiz Gary M. Leuty Hao Guo Abdol Hadi Mokarizadeh and Joao M. Maia.

Non-reactive facet specific adsorption as a route to remediation of chlorinated organic contaminants (2023)
The present work quantifies metal-contaminant interactions between palladium substrates and three salient chlorinated organic contaminants, namely trichloroethylene 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene (TCB), and 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl (PCB77). Given that Pd is one of the conventional catalytically active materials known for contaminant removal, maximizing catalytic efficiency through optimal adsorption dynamics reduces the cost of remediation of contaminants that are persistent water pollutants chronically affecting public health. Adsorption efficiency analyses from all-atom molecular dynamics (MD) simulations advance the understanding of reaction mechanisms available from density functional theory (DFT) calculations to an extractable feature scale that can fit the parametric design of supported metal catalytic systems and feed into high throughput catalyst selection. Data on residence time, site-specific adsorption, binding energies, packing geometries, orientation profiles, and the effect of adsorbate size show the anomalous behaviour of organic contaminant adsorption on the undercoordinated {110} surface as compared to the {111} and {100} surfaces. The intermolecular interaction within contaminants from molecular dynamics simulation exhibits refreshing results than ordinary single molecule density functional theory calculation. Since complete adsorption and dechlorination is an essential step for chlorinated organic contaminant remediation pathways, the presented profiles provide essential information for designing efficient remediation systems through facet-controlled palladium nanoparticles. The research was conducted by Hao Guo, Emily A. Gerstein, Kshitij C.Jha, Iskinder Arsano, M.Ali Haider, and Tuhin S.Khan.

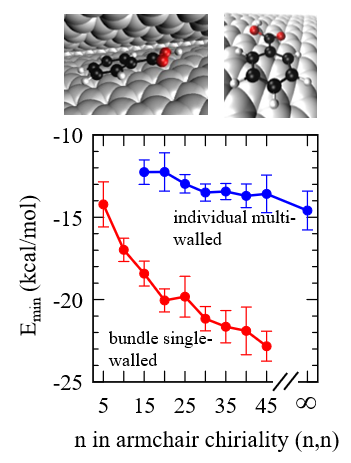
High Adsorption of Benzoic Acid on Single Walled Carbon Nanotube Bundles (2020)
In the second of a four-parter a large collaborative group reports on the high adsorption capacity of single-walled carbon nanotubes. The measured sorption capacity from isotherm studies revealed contaminant retention capacity as high as 375 mg/g. This is higher that would be expected for activated carbon cloth, modified bentonite, and commercially available graphitized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Simulations were designed to imitate the observed stable bundle formation in single-walled carbon nanotube arrangements, and to then contrast the adsorption behavior with that on the surfaces of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Groove adsorption was found to be the likely cause of the experimentally observed high sorption. The research was conducted by Li, De Silva, Arsano, and 9 other authors, and published in Nature Scientific Reports.

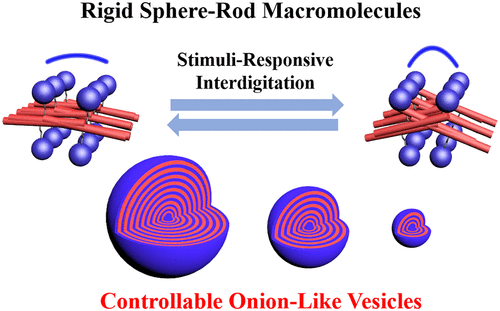
Departing from the common approach of producing curvatures in onion-like vesicles by chain bending of flexible molecules, a new work by Luo, Liu and collaborators employs hybrid macromolecules of hydrophilic rigid spheres and hydrophobic rod-like oligofluorenes to achieve solution-condition induced size (curvature) controllability of the vesicles. The work importantly extends to associated aspects such as thermo-reversibility, effect of charge, and nature of hybrid architecture.

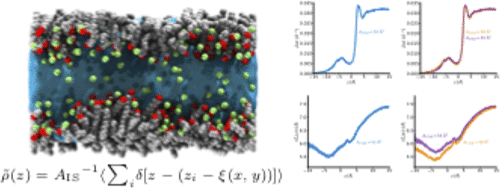
Structure and Dynamics of Nanoconfined Water between Surfactant Monolayers (2019)
All-atom molecular dynamics (MD) simulations out of a King’s College London – University of Akron collaborative work by Ziolek, Fraternali and others reveal interesting physical behaviors of water confined between surfactant-containing monolayers. The density, mobility, and ordering of confined water is sensitive to the amount of surfactant in the monolayers. Strikingly, the authors, observe the emergence of noncentrosymmetry when water is confined between monolayers of different surfactant loading.

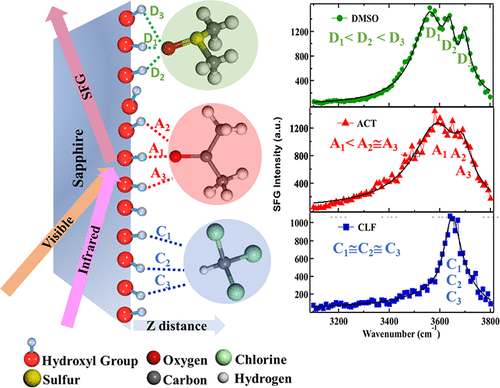
Interaction Geometry Causes Spectral Line-Shape Broadening at the Solid/Liquid Interface (2019)
A study on interfacial acid-base interactions has recently been published by Kumar, Kaur and co-workers. Combining surface-sensitive sum frequency generation spectroscopy (SFG) and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations the authors characterize the interaction of liquid molecules with hydroxylated solid surfaces. With sapphire as substrate the authors observe interaction energies of polar molecules varying from weak to strong, and attribute this to geometric constraints on planar surfaces as opposed to effects from adsorption orientation or surface roughness.

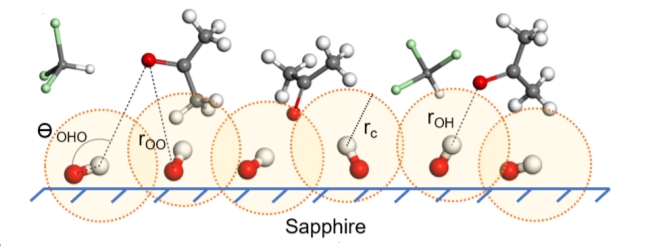
Kumar, Singla, and coworkers employed computational methods to provide one of the more atomically detailed presentations in the literature so far in the attempt to understand the behavior of a binary mixture close of a substrate of materials science interest. The substrate studied is sapphire, and the mixture is one comprised of acetone and chloroform. The paper details how the components of the mixture influence each other’s interaction with sapphire. This is a collaborative work between the Dhinojwala and Tsige groups in the Department of Polymer Science. Readers are encouraged to go to the original article for a fuller discussion of the findings as well as for helpful graphics.

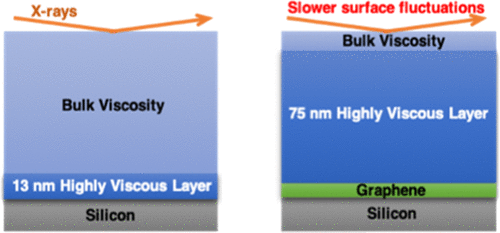
Proximity to Graphene Dramatically Alters Polymer Dynamics (2019)
The distinctive conformation of PS chains near silicone versus near graphene is accompanied by a major reduction of thermally stimulated fluctuations in the case of the latter. The authors, Yang, Presto, and others, determine that this effect is due to “a layer of highly viscous polymer next to the substrate being thicker for graphene (75 nm or 7.5Rg) than for silicon (13 nm or 1.3Rg)”. The article can be viewed/downloaded here.

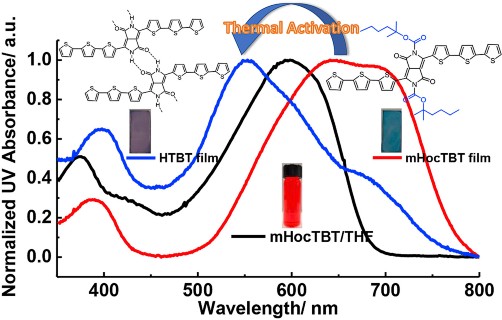
Work by Kun Yang et al., published in the journal Polymer, investigates hydrogen-bonding mediated molecular packing in solid state. The study was made via synthesis and characterization of two oligomers.

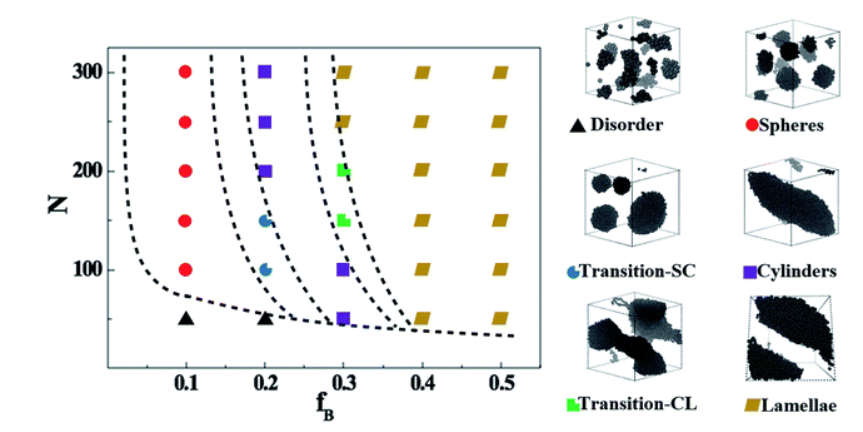
Phase Manipulation of Topologically Engineered AB Type Multi-Block Copolymers (2019))
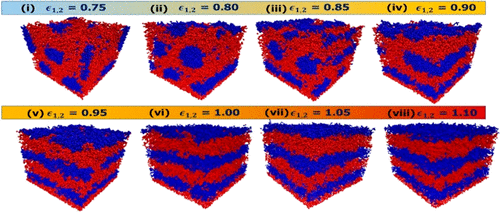
Sai Li, Wei Tao et al. investigated four typical multi-block copolymers (MBCPs) systems filled with nanoparticles (NPs). Design and fabrication of high performance BCPs can be greatly informed by the understanding of how ordered phases can be altered on demand. This work studied, among other things, the dependence of order-to-order transition (OOT) behavior on the strength of repulsive interactions, temperature, and periodic dynamic shearing, as well as quantified the increase in branch density leading to the occurrence of phase transition.

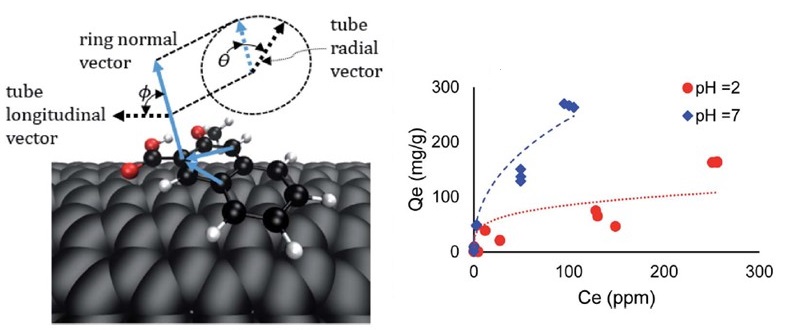
Carbon nanotubes are in vogue for a multitude of nanotechnological applications, and for good reasons. The first of a series of papers from a collaborative work among the Tisge group, the Ma group at Texas A&M, and the Talapatra group at Southern Illinois, Carbondale, was published by Li, Arsano, and coworkers. The paper reports how different molecular forces between contaminants and the surfaces of carbon nanotubes help or hurt targeted adsorption of contaminants in water. The diversity of contaminant molecules investigated is quite a departure from similar previous works. Please find the full article by going to the publisher’s website, or by placing a direct request to the authors.

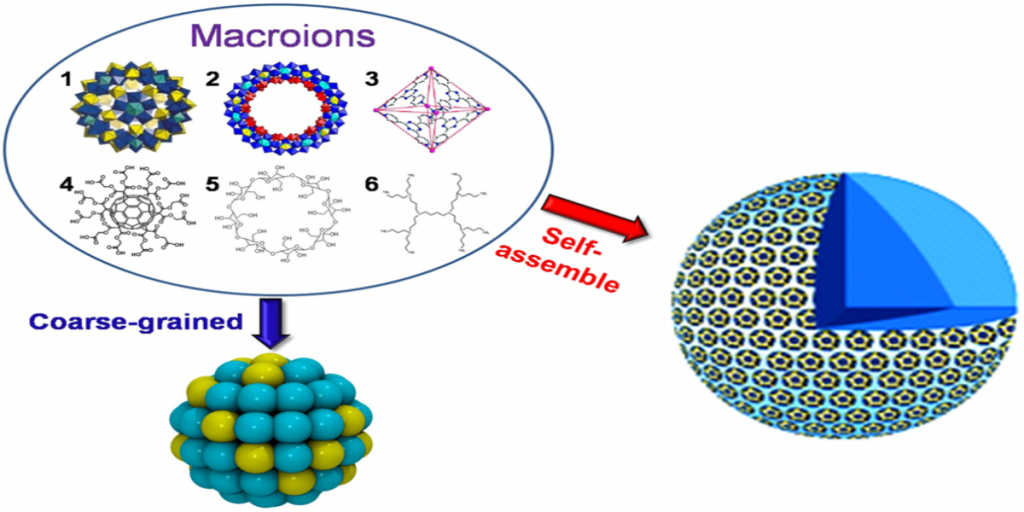
Why 3-D symmetrical macroions prefer to form 2-D monolayers in bulk solution can be explained by macroion surface charge distribution. This study, with implications for diverse materials and biological phenomena, was published in the journal Nature Scientific Reports.

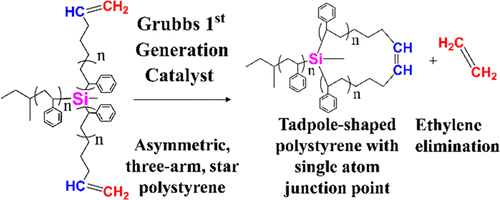
An ACS Macromolecules paper reports loss of an ethylene unit in a tadpole-shaped polystyrene with a single atom junction point compared to its corresponding asymmetric, three-arm, star precursor. MD simulations find a smaller hydrodynamic volume for the tadpole-shaped PS as compared to the three-arm star precursor, in quantitative agreement with GPC results.

Solvent and Substrate Induced Synergistic Ordering in Block Copolymer Thin Films (2018)
A novel coarse-grained molecular dynamics approach proves useful in helping understand ordering and morphology in solvent swollen thin block copolymer films. Arvind Modi and collaborators point their finger at the sensitivity of solvent-block interactions in generating several kinds of morphologies. More about this work can be found here.

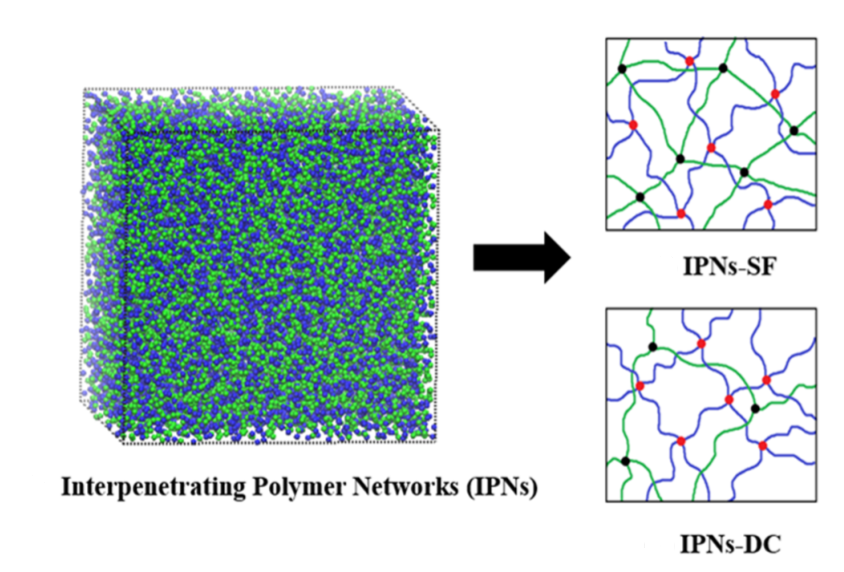
How can mechanical properties of polymeric networks such as stress relaxation and uniaxial tension be described using Time-Temperature and Frequency-Temperature Superposition Principles? How do effects such as temperature regime and network type influence the applicability of these principles? Wei Tao and co-authors address these questions in a paper published in the Journal of Chemical Physics.

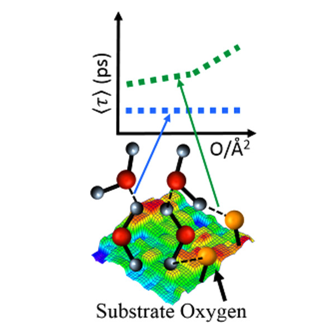
Characterizing the Hydrophobicity of Surfaces Using the Dynamics of Interfacial Water Molecules
(2018)
Water in contact with a model polymer surface of atactic polystyrene exhibits very interesting but dissimilar properties depending on whether it forms hydrogen bonding with the polymer surface . In the absence of hydrogen bonding fast water dynamics were registered. The presence of hydrogen bonding, on the other hand, dictates a measurable dependence of dynamics on surface polarity. Selemon Bekele and Mesfin Tsige published their findings in the Journal of Physical Chemistry.

Other Recent Publications
Duki, Solomon F., and Mesfin Tsige. “Volume analysis of supercooled water under high pressure.” MRS Advances(2018): 1-12.
Negash, Solomon, Yergou B. Tatek, and Mesfin Tsige. “Effect of tacticity on the structure and glass transition temperature of polystyrene adsorbed onto solid surfaces.” The Journal of chemical physics 148, no. 13 (2018): 134705.
Gaitho, Francis M., Mesfin Tsige, Genene T. Mola, and Giuseppe Pellicane. “Surface Segregation of Cyclic Chains in Binary Melts of Thin Polymer Films: The Influence of Constituent Concentration.” Polymers 10, no. 3 (2018): 324.
Jiang, Naisheng, Mani Sen, Maya K. Endoh, Tadanori Koga, Elin Langhammer, Patrik Bjöörn, and Mesfin Tsige. “Thermal properties and segmental dynamics of polymer melt chains adsorbed on solid surfaces.” Langmuir 34, no. 14 (2018): 4199-4209.
Liu, Zhuonan, Xiaoxiao Li, Yexin Zheng, Shi-Qing Wang, and Mesfin Tsige. “Chain Network: Key to the Ductile Behavior of Polymer Glasses.” Macromolecules 51, no. 5 (2018): 1666-1673.
Liu, Zhuonan, Xiaoxiao Li, Yexin Zheng, Shi-Qing Wang, and Mesfin Tsige. “Chain Network: Key to the Ductile Behavior of Polymer Glasses.” Macromolecules 51, no. 5 (2018): 1666-1673.
Jha, Kshitij C., Alexander Weber, Yeneneh Y. Yimer, and Mesfin Tsige. “Soft Templating of Water Aggregates Disrupts π–π Stacking in Crystalline Poly (3-hexylthiophene).” The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 122, no. 1 (2017): 422-428.
Jha, Kshitij C., Selemon Bekele, Ali Dhinojwala, and Mesfin Tsige. “Hydrogen bond directed surface dynamics at tactic poly (methyl methacrylate)/water interface.” Soft matter 13, no. 45 (2017): 8556-8564.
Zheng, Zijian, Guanyi Hou, Xiuyang Xia, Jun Liu, Mesfin Tsige, Youping Wu, and Liqun Zhang. “Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Polymer Nanocomposites with Controllable Dispersion of Spherical Nanoparticles.” The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 121, no. 43 (2017): 10146-10156.
Miao, Jiayuan, Darrell H. Reneker, Mesfin Tsige, and Philip L. Taylor. “Molecular dynamics simulations and morphology analysis of TEM imaged PVDF nanofibers.” Polymer 125 (2017): 190-199.
Miao, Jiayuan, Mesfin Tsige, and Philip L. Taylor. “Generalized model for the diffusion of solvents in glassy polymers: From Fickian to Super Case II.” The Journal of chemical physics147, no. 4 (2017): 044904.
Zhang, Haichang, Kun Yang, Yu‐Ming Chen, Ram Bhatta, Mesfin Tsige, Stephen ZD Cheng, and Yu Zhu. “Polymers Based on Benzodipyrrolidone and Naphthodipyrrolidone with Latent Hydrogen‐Bonding on the Main Chain.” Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics 218, no. 13 (2017): 1600617.
Li, Dong, Zhuonan Liu, Jie Song, Hui Li, Baofang Zhang, Panchao Yin, Zhaoxiong Norm Zheng et al. “Cation Translocation around Single Polyoxometalate–Organic Hybrid Cluster Regulated by Electrostatic and Cation–π Interactions.” Angewandte Chemie 129, no. 12 (2017): 3342-3346.
Megnidio-Tchoukouegno, M., F. M. Gaitho, G. T. Mola, M. Tsige, and G. Pellicane. “Unravelling the surface composition of symmetric linear-cyclic polymer blends.” Fluid Phase Equilibria 441 (2017): 33-42.
Li, Dong, Zhuonan Liu, Jie Song, Hui Li, Baofang Zhang, Panchao Yin, Zhaoxiong Norm Zheng et al. “Cation Translocation around Single Polyoxometalate–Organic Hybrid Cluster Regulated by Electrostatic and Cation–π Interactions.” Angewandte Chemie 129, no. 12 (2017): 3342-3346.
Jha, Kshitij C., Vikram Singh, and Mesfin Tsige. “Interfacial Engineering for Oil and Gas Applications: Role of Modeling and Simulation.” In New Frontiers in Oil and Gas Exploration, pp. 257-283. Springer, Cham, 2016.
Tchoukouegno, Mireille M., Giuseppe Pellicane, Mesfin Tsige, and Genene Tessema Mola. “Nano-scale morphology dependent performance of thin film organic solar cells.” Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 28, no. 1 (2017): 214-221.
Jha, Kshitij C., Zhuonan Liu, Hema Vijwani, Mallikarjuna Nadagouda, Sharmila M. Mukhopadhyay, and Mesfin Tsige. “Carbon Nanotube Based Groundwater Remediation: The Case of Trichloroethylene.” Molecules 21, no. 7 (2016): 953.
Bekele, Selemon, and Mesfin Tsige. “Effect of polymer/solid and polymer/vapor instantaneous interfaces on the interfacial structure and dynamics of polymer melt systems.” Langmuir32, no. 28 (2016): 7151-7158.
Liu, Zhuonan, Tianbo Liu, and Mesfin Tsige. “Elucidating the origin of the attractive force among hydrophilic macroions.” Scientific reports 6 (2016): 26595.
Pellicane, Giuseppe, Mireille Megnidio-Tchoukouegno, Genene T. Mola, and Mesfin Tsige. “Surface enrichment driven by polymer topology.” Physical Review E 93, no. 5 (2016): 050501.
Leuty, Gary M., Mesfin Tsige, Gary S. Grest, and Michael Rubinstein. “Tension amplification in tethered layers of bottle-brush polymers.” Macromolecules 49, no. 5 (2016): 1950-1960.
Jha, Kshitij C., Emmanuel Anim-Danso, Selemon Bekele, George Eason, and Mesfin Tsige. “On modulating interfacial structure towards improved anti-icing performance.” Coatings6, no. 1 (2016): 3.
Jha, Kshitij C., Ali Dhinojwala, and Mesfin Tsige. “Local structure contributions to surface tension of a stereoregular polymer.” ACS Macro Letters 4, no. 11 (2015): 1234-1238.
Pellicane, Giuseppe, Mesfin Tsige, and Berhanu Aragie. “Thermodynamics of a stochastic three level elevator model.” The European Physical Journal B 88, no. 11 (2015): 307.
Bhatta, Ram S., and Mesfin Tsige. “Understanding structural and electronic properties of dithienyl benzothiadiazole and its complex with C70.” Polymer 75 (2015): 73-77.
Yimer, Yeneneh Y., Brandon Yang, Ram S. Bhatta, and Mesfin Tsige. “Interfacial and wetting properties of poly (3-hexylthiophene)–water systems.” Chemical Physics Letters635 (2015): 139-145.
Bhatta, Ram S., Giuseppe Pellicane, and Mesfin Tsige. “Tuning range-separated DFT functionals for accurate orbital energy modeling of conjugated molecules.” Computational and Theoretical Chemistry 1070 (2015): 14-20.
Liu, Chang, Chao Yi, Kai Wang, Yali Yang, Ram S. Bhatta, Mesfin Tsige, Shuyong Xiao, and Xiong Gong. “Single-junction polymer solar cells with over 10% efficiency by a novel two-dimensional donor–acceptor conjugated copolymer.” ACS applied materials & interfaces 7, no. 8 (2015): 4928-4935.
Bhatta, Ram S., and Mesfin Tsige. “Structural dependence of electronic properties in AADAA-type organic solar cell material.” International Journal of Photoenergy 2015 (2015).
Yimer, Yeneneh Y., Brandon Yang, Ram S. Bhatta, and Mesfin Tsige. “Interfacial and wetting properties of poly (3-hexylthiophene)–water systems.” Chemical Physics Letters635 (2015): 139-145.